| Active Ingredient | TUCATINIB |
|---|
| Drug Name | FDA Application No. | Company | Dosage Form;Route | Strength | RLD Strength | Original Approval or Tentative Approval Date |
Exclusivity Expiration (NCE) |
Exclusivity Expiration (ODE) |
Chemical Type |
Review Classification |
Marketing Status |
TE Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TUKYSA | 213411 | SEAGEN INC | TABLET;ORAL | 50MG, 150MG | 150MG | April 17, 2020 | April 17, 2025 | April 17, 2027 | Type 1 - New Molecular Entity | PRIORITY; Orphan | Prescription | None |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Structural Formula |
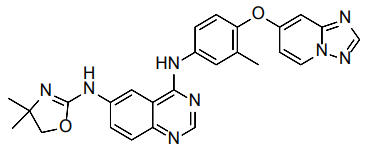 |
| Chemical Name | (N4-(4-([1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-7-yloxy)-3 methylphenyl)-N6-(4,4-dimethyl-4,5-dihydrooxazol-2-yl)quinazoline-4,6-diamine |
| CAS No | 937263-43-9 |
| Molecular Formula | C26H24N8O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 480.52 g/mol |
| Appearance | Off-white to yellow, non-hygroscopic crystalline powder |
| Solubility | It is practically insoluble in water; in aqueous buffer solutions at pH above 4 it has low solubility (<0.4 mg/ml); below pH 4 the active substance exhibits high solubility (>18.9 mg/ml). |
| Water Solubility | 0.004 mg/mL |
| Polymorphism | Polymorphism has been observed for tucatinib. It has been found to exist in many solid-state forms: 4 crystalline anhydrous polymorphs and 25 crystalline pseudopolymorphs have been characterised to date. Of the 25 pseudopolymorphs, 3 hydrates, 6 classical-type solvates, 1 transient solvate and 3 unique isostructural solvates composing 15 solvates have been identified. Crystalline solvate form (form B) tucatinib hemiethanolate was selected for further development due favourable physicochemical properties. Tucatinib hemiethanolate (form B) is obtained consistently by the manufacturing process. It has been demonstrated that there is no change in polymorphic form of the active substance during AS storage. |
| pKa (Strongest Acidic) | 17.08 |
| pKa (Strongest Basic) | 4.57 |
| Log P | 3.87, 5.25 |
| Identification | (HPLC,FT-IR |
| Degradation | Stress testing of the AS was performed to evaluate degradation of the AS and the stability indicating capability of the AS HPLC assay and purity method. These studies were conducted using a commercial scale batch placed under a variety of stressed conditions including acidic, basic, oxidative, aqueous, and thermal stress. It was also concluded that the HPLC assay and purity method is stability indicating. |
| Hygroscopic | Non-hygroscopic |
| Photostability study | Photostability testing was carried out on one commercial scale batch in as per ICH Q1B. No degradation was found in the light-exposed and the controlled samples after the exposure, indicating that AS is not light sensitive. |
| Melting Point | 230 |
| BCS Class | BCS Class II |
| Manufacture of API | The synthesis of tucatinib hemiethanolate consists in total of six steps. To the starting materials initially proposed by the applicant, another one was designated upon the request of the CHMP. All SMs have been justified in line with the considerations of ICH Q11 and are acceptable. The SMs are controlled by acceptable specifications. Isolated intermediates in the synthesis are clearly defined and are sufficiently characterised and controlled by appropriate specifications. |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Indications and Usage | TUKYSA is a kinase inhibitor indicated in combination with trastuzumab and capecitabine for treatment of adult patients with advanced unresectable or metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer, including patients with brain metastases, who have received one or more prior anti-HER2-based regimens in the metastatic setting. |
| Dosage and Administration | Recommended dosage: 300 mg taken orally twice daily with or without food. For patients with severe hepatic impairment, the recommended dosage is 200 mg orally twice daily. |
| Mechanism of action | Tucatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor of HER2. In vitro, tucatinib inhibits phosphorylation of HER2 and HER3, resulting in inhibition of downstream MAPK and AKT signaling and cell proliferation, and showed antitumor activity in HER2 expressing tumor cells. In vivo, tucatinib inhibited the growth of HER2 expressing tumors. The combination of tucatinib and trastuzumab showed increased anti-tumor activity in vitro and in vivo compared to either drug alone. |
| Absorption | The median time to peak plasma concentration of tucatinib was approximately 2 hours (range 1 to 4 hours). |
| Food Effect | Following administration of a single oral dose of TUKYSA in 11 subjects after a high-fat meal (approximately 58% fat, 26% carbohydrate, and 16% protein), the mean AUC0-INF increased by 1.5-fold, the Tmax shifted from 1.5 hours to 4 hours, and Cmax was unaltered. The effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of tucatinib was not clinically meaningful. |
| Distribution | The geometric mean (CV%) apparent volume of distribution of tucatinib was approximately 1670 L (66%). The plasma protein binding was 97.1% at clinically relevant concentrations. |
| Metabolism | Tucatinib is metabolized primarily by CYP2C8 and to a lesser extent via CYP3A. |
| Elimination | Excretion: Following a single oral dose of 300 mg radiolabeled tucatinib, approximately 86% of the total radiolabeled dose was recovered in feces (16% of the administered dose as unchanged tucatinib) and 4.1% in urine with an overall total recovery of 90% within 13 days post-dose. In plasma, approximately 76% of the plasma radioactivity was unchanged, 19% was attributed to identified metabolites, and approximately 5% was unassigned. Elimination : The geometric mean (CV%) half-life of tucatinib was approximately 8.5 (21%) hours and apparent clearance was 148 L/h (55%). |
| Peak plasma time (Tmax) | 2 hours (range 1 to 4 hours). |
| Half life | 8.5 (21%) hours |
| Bioavailability | - |
| Age, gender | Age (< 65 (n =211); ≥ 65 (n = 27)), albumin (25 to 52 g/L), creatinine clearance (creatinine clearance [CLcr] 60 to 89 mL/min (n = 89); CLcr 30 to 59 mL/min (n = 5)), body weight (41 to 138 kg), and race (White (n=168), Black (n=53), or Asian (n=10)) did not have a clinically meaningful effect on tucatinib exposure. |
| DMF | Status | Type | Submit Date | Holder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not Available | ||||
| Parameters | Details | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | 50mg | 150mg | |
| Excipients used | Copovidone, crospovidone, sodium chloride, potassium chloride, sodium bicarbonate, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose | ||
| Composition of coating material | Yellow film coat: polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide, macrogol/polyethylene glycol, talc, and yellow iron oxide non-irradiated | ||
| Composition of caspule shell | NA | ||
| Pharmaceutical Development |
The qualitative composition of Tukysa is presented in section 2.2.1 of this report and in SmPC section 6.1. All excipients used are standard and are commonly used in the pharmaceutical industry. The list of excipients is included in section 6.1 of the SmPC and in paragraph 2.1.1 of this report. The two strengths are dose proportional apart from a small difference in the amount of film-coating. The filmcoating is non-functional. The development of the formulation and manufacturing process was conducted following a traditional pharmaceutical development approach that targeted an immediate release oral product. However, principles of enhanced approach as described in ICH Q8 through Q11 such as definition critical quality attributes (CQAs) as well as formulation and process risk assessments have been utilised in formulation and process development, but no design spaces have been claimed.Tucatinib is a BCS Class 2 compound exhibiting low aqueous solubility and high permeability. Earlyclinical studies used two different powder in capsule formulations and two different micronised powder in suspension formulations. The development and selection of the formulation was driven by the early formulations used initially in the clinical development. Different formulations containing tucatinib hemiethanolate were used and compared in clinical studies: powder in capsule, micronised powder in capsule, suspension of micronised active substance, solution of active substance and amorphous tablet formulation, respectively. The observed high inter-subject pharmacokinetic variability and an effect on absorption of tucatinib when administered in the fed state, triggered further development work evaluating enabling formulations of tucatinib. No AS concentrations used in manufacturing process are above the equilibrium solubility limits. The development of the formulation was described in detail. A discussion of the different solvent systems evaluated, and lots produced from each solvent system were provided. The final solvent system was selected to minimise residual water and reduce the risk for potential hydrolysis of tucatinib. This solvent system was used throughout clinical development at the commercial manufacturing site and remains unchanged for the proposed commercial process. During manufacture of the intermediate, the AS is converted from tucatinib hemiethanolate (crystalline polymorphic form B) to tucatinib (amorphous form). In order to ensure the immediate release of drug, the tablet formulation include crospovidone as a disintegrant and multiple disintegrant aids to achieve rapid disintegration to particles or small granules, thereby facilitating rapid dissolution. A dry granulation is employed to improve the flowability, particle size uniformity, and compressibility of the powder blend. The amount of intermediate is adjusted based on its potency with concomitant equivalent adjustments to the weights of sodium chloride, potassium chloride, and sodium bicarbonate. Two complementary dissolution methods, method 1 and method 2, are used to control the finished product. Dissolution method 1 was included in the initial dossier, while dissolution method 2 was introduced during the procedure following a major objection raised by CHMP concerning the discriminatory power of method 1. The development of both dissolution methods has been sufficiently described and justified. The proposal for the combination of two dissolution methods and their corresponding limits for the control of the finished product has been adequately supported by development data; the approach is acceptable. Dissolution method 1 has not been demonstrated to be discriminatory with regards to the most critical attributes in the finished product, which are the form of the active substance and the particle size of the intermediate. Since the data presented clearly demonstrates that the dissolution method cannot differentiate between the proposed formulation containing the AS in the amorphous form and a formulation containing 100% crystalline AS, the use of the method to waive any bioequivalence testing in the future is not an option. Based on the dissolution profiles/data presented, the proposed acceptance criteria for dissolution of (method 1) has been justified. Dissolution method 2 has been demonstrated to be discriminatory with regards to different concentrations of crystalline content, minor composition quantitative changes and hardness of the filmcoated tablets. Based on the development data and the test of the pivotal batches and the primary stability batches, the proposed acceptance criterion for dissolution (method 2) has been justified. However, since this acceptance criterion was based on limited batch data and stability data, the CHMP requested, and the applicant has made, the following commitments: 1) to re-evaluate the specification limit for dissolution (method 2) when data from 30 finished product batches and at least 12 months of stability data are available is available post-approval and 2) to submit updated batch analysis data and stability data for the finished product analysed with the complementary dissolution method 2 when data is available post-approval; this approach is accepted (See 3.1.6).The formulation and manufacturing process of the finished product have remained the same throughout clinical development and remain unchanged for the proposed commercial process. The sites involved in the development and the history of finished product batches produced throughout clinical development including manufacture of the primary stability batches was presented. A process risk assessment to assess the potential impact of manufacturing process unit operations critical quality attributes (CQAs) has been performed. The process steps feed solution preparation, spray drying and secondary drying and their potential impact on each CQA (assay, related substances,crystallinity, residual solvents, water content and PSD) have been investigated. The proposed PARs have been justified. For the film-coated tablets, an initial risk assessment was performed to assess the potential impact of manufacturing process unit operations on tucatinib CQAs and a summary was presented. The chosen CQAs are justified and are all included and controlled in the product specification as discussed later in the report. The unit operations pre-blending, roller compaction, final blending, tablet compression, and film- coating were considered to have a medium overall risk to influence tablet CQAs, and therefore evaluation of the process parameters of these unit operations were evaluated in DOE studies. Based on these investigations PARs for process parameters of each unit operation have been established. The development of the control strategy for tucatinib film-coated tablets has been described in sufficient detail. |
||
| Manufacture of the product |
The manufacturing process is divided into the manufacture of the intermediate and the manufacture of the film-coated tablets. The manufacturing process for the intermediate comprises four steps. A flowchart including the applied IPCs was presented. The manufacturing process was described in sufficient detail including conditions/parameters and equipment used. The IPCs have been described including methods and acceptance criteria. The PARs have been set according to the results obtained during pharmaceutical development. No critical process parameters were identified. The release and stability specifications for the intermediate cover relevant parameters for this finished product intermediate and are suitable to control its quality. Sufficient batch analysis data were provided for the intermediate. |
||
| Tablet / Capsule Image |

|

|
|
| Appearance | Yellow, film-coated, round tablets containing 50 mg of tucatinib. Each tablet is debossed with “TUC” on one side and “50” on the other side | yellow, film-coated, oval-shaped tablets containing 150 mg of tucatinib. Each tablet is debossed with “TUC” on one side and “150” on the other side | |
| Imprint code / Engraving / Debossment | Debossed with “TUC” on one side and “50” on the other side | Debossed with “TUC” on one side and “150” on the other side | |
| Score | Non score | Non score | |
| Color | Yellow | Yellow | |
| Shape | Round | Round | |
| Dimension | - | - | |
| Mfg by |
Seattle Genetics, Inc. Bothell, WA 98021 1-855-4SEAGEN |
||
| Mfg for | - | ||
| Marketed by | - | ||
| Distributed by | - | ||
| Application No. | Prod No | Patent No | Patent Expiration | Drug Substance Claim | Drug Product Claim | Patent Use Code | Delist Requested | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N213411 | 1, 2 | 7452895 | November 16, 2024 | DS | DP | U-2788 | - | Download |
| N213411 | 1, 2 | 8648087 | December 4, 2031 | DS | DP | - | - | Download |
| N213411 | 1, 2 | 9457093 | December 10, 2032 | - | DP | U-2788 | - | Download |
| N213411 | 1, 2 | 9693989 | September 5, 2027 | - | DP | U-2788 | - | Download |
| USP Apparatus | Speed (RPMs) | Medium | Volume (mL) | Recommended Sampling Times (minutes) | Date Updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II (Paddle) | 75 rpm | 0.1 M citrate buffer, pH 3.4, containing 0.05% Brij 35 | 900ml | 10, 15, 20, 30, 45, 60 minutes | As per SBOA |
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| FDA label | Download |
| FDA chemistry review | Download |
| FDA Pharmacology Review(s) | Download |
| FDA Clinical Pharmacology Biopharmaceutics Review(s) | Download |
| FDA BE Recommendation | |
| European Public Assessment Report | Download |
| Territory | Brand name / Generic company name | Link |
|---|---|---|
| EU | TUKYSA | Download |
| UK | - | |
| US | TUKYSA | Download |
| - |
| www.accessdata.fda.gov, www.drugbank.ca, www.ema.europa.eu, www.medicines.org.uk, dailymed.nlm.nih.gov |
