| Active Ingredient | SORAFENIB TOSYLATE |
|---|
| Drug Name | FDA Application No. | Company | Dosage Form;Route | Strength | RLD Strength | Original Approval or Tentative Approval Date |
Exclusivity Expiration (NCE) |
Exclusivity Expiration (ODE) |
Chemical Type |
Review Classification |
Marketing Status |
TE Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEXAVAR | (NDA) 021923 | BAYER HLTHCARE | TABLET;ORAL | EQ 200MG BASE | EQ 200MG BASE | December 20, 2005 | _ | Nov 22, 2020 | 1 New molecular entity (NME) | P Priority review drug O Orphan drug | Prescription | None |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Structural Formula |
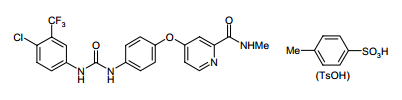 |
| Chemical Name | 4-(4-{3-[4-Chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ureido}phenoxy)N2methylpyridine-2-carboxamide 4-methylbenzenesulfonate |
| CAS No | 284461-73-0 |
| Molecular Formula | C 21H16ClF 3N4O3 x C7H8O3S |
| Molecular Weight | 637.0 g/mole |
| Appearance | White to yellowish or brownish solid |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble in ethanol and soluble in PEG 400. Slightly soluble in alcohols and soluble in DMSO and DMF. |
| Water Solubility | Practically insoluble in water. 0.00171 mg/mL(Predicted) |
| Polymorphism | IT is exhibits polymorphism and it crystallizes in three different modifications (Mod I, Mod II and Mod III) |
| pKa (Strongest Acidic) | 11.55 (Predicted) |
| pKa (Strongest Basic) | 2.03 Predicted) |
| Log P | 3.8 |
| Identification | HPLC and NIR |
| Degradation | Stable |
| Hygroscopic | - |
| Photostability study | Slightly sensitive to light |
| Melting Point | - |
| BCS Class | II |
| Manufacture of API | Sorafenib tosylate is synthesised in six steps. The manufacture involves the synthesis of a key isolated intermediate, which is synthesized viathree reaction steps, from the starting material. The next two steps involve the formation of sorafenib followed bythe salt formation and crystallisation, resulting in sorafenib tosylate. The final step involves micronization in an air-jet mill. |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Indications and Usage | NEXAVAR is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of Unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma Advanced renal cell carcinoma Locally recurrent or metastatic, progressive, differentiated thyroid carcinoma refractory to radioactive iodine treatment |
| Dosage and Administration |
400 mg (2 tablets) orally twice daily without food. Treatment interruption and/or dose reduction may be needed to manage suspected adverse drug reactions. |
| Mechanism of action | Sorafenib is a kinase inhibitor that decreases tumor cell proliferation in vitro. Sorafenib was shown to inhibit multiple intracellular (c-CRAF, BRAF and mutant BRAF) and cell surface kinases (KIT, FLT-3, RET, RET/PTC, VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, and PDGFR-ß). Several of these kinases are thought to be involved in tumor cell signaling, angiogenesis and apoptosis. Sorafenib inhibited tumor growth of HCC, RCC, and DTC human tumor xenografts in immunocompromised mice. Reductions in tumor angiogenesis were seen in models of HCC and RCC upon sorafenib treatment, and increases in tumor apoptosis wer e obser ved in models of HCC, RCC, and DTC. |
| Absorption | After administration of NEXAVAR tablets, the mean relative bioavailability was 38–49% when compared to an oral solution. Following oral administration, sorafenib reached peak plasma levels in approximately 3 hours. With a moderate-fat meal (30% fat; 700 calories). |
| Food Effect | Bioavailability was similar to that in the fasted state. With a high-fat meal (50% fat; 900 calories), bioavailability was reduced by 29% compared to that in the fasted state. It is recommended that NEXAVAR be administered without food. |
| Distribution | Mean C max and AUC increased less than proportionally beyond oral doses of 400 mg administered twice daily. In vitro binding of sorafenib to human plasma proteins was 99.5%. |
| Metabolism |
Sorafenib undergoes oxidative metabolism by hepatic CYP3A4, as well as glucuronidation by UGT1A9. Inducers of CYP3A4 activity can decrease the systemic exposure of sorafenib. Sorafenib accounted for approximately 70–85% of the circulating analytes in plasma at steady-state. Eight metabolites of sorafenib have been identified, of which 5 have been detected in plasma. The ma in circulating metabolite of sorafenib, the pyridine N-oxide that comprises approximately 9–16% of circulating analytes at steady-state, showed in vitro potency similar to that of sorafenib. |
| Elimination | Following oral administration of a 100 mg dose of a solution formulation of sorafenib, 96% of the dose was recovered within 14 days, with 77% of the dose excr eted in feces and 19% of the dose excr eted in urine as glucuronidated metabolites. Unchanged sorafenib, accounting for 51% of the dose, was found in feces but not in urine. |
| Peak plasma time (Tmax) | 3 hours |
| Half life | 25 to 48 hours |
| Bioavailability | 38–49% |
| Age, gender | A study of the pharmacokinetics of sorafenib indicated that the mean AUC of sorafenib in Asians (N=78) was 30% lower than in Caucasians (N=40). Gender and age do not have a clinically meaningful effect on the pharmacokinetics of sorafenib. |
| DMF | Status | Type | Submit Date | Holder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24578 | I | II | March 10, 2011 | NATCO PHARMA LTD |
| 26460 | A | II | September 18, 2012 | SICHUAN XIELI PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD |
| 26693 | A | II | December 21, 2012 | NATCO PHARMA LTD |
| 27793 | I | II | November 20, 2013 | ZHEJIANG JIUZHOU PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD |
| 28556 | A | II | September 23, 2014 | RELIANCE LIFE SCIENCES PVT LTD |
| 29340 | A | II | June 30, 2015 | YABAO PHARMACEUTICAL GROUP CO LTD |
| 29941 | A | II | November 29, 2015 | ALEMBIC PHARMACEUTICALS LTD |
| 30180 | A | II | January 30, 2016 | MSN LABORATORIES PRIVATE LTD |
| 30234 | A | II | February 23, 2016 | TEVA PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRIES LTD |
| 30235 | A | II | January 28, 2016 | HETERO LABS LTD |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Strength | EQ 200MG BASE |
| Excipients used |
Croscarmellose sodium, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium lauryl sulphate, magnesium stearate |
| Composition of coating material | Polyethylene glycol, titanium dioxide and ferric oxide red, hypromellose |
| Composition of caspule shell | - |
| Pharmaceutical Development |
Sorafenib tosylate (274 mg) equivalent to 200 mg of sorafenib. Due to the very low solubility of sorafenib in aqueous media, the tosylate salt was used in the drug product. To enhance dissolution the active substance is micronized and the particle size is tightly controlled. The permeability of sorafenib tosylate using the Caco-2 cell model indicates that it is a ‘high permeability’ compound. The objective of the pharmaceutical development has been to obtain a small immediate release tablet with a high amount of active substance. Sorafenib tosylate exhibited good compression characteristics and therefore a high content of drug could be used in the formulation. A wet granulation process with water as granulating liquid was found to be suitable. The content of magnesium stearate in the debossed tablet was adjusted to avoid sticking to the tabletting tools. The tablets are film coated to facilitate swallowing and to add colour. |
| Manufacture of the product | The manufacture of the finished product involves conventional processes including (1) mixing, (2) wet high-shear granulation, (3) wet sizing, (4) drying of granulate, (5) tablet compression and (6) film-coating.The dissolution rate was determined to be a critical property of the product and to be affected by several manufacturing conditions. The potential for polymorphism was investigated by Raman spectroscopy and found to be unchanged. |
| Tablet / Capsule Image |

|
| Appearance | Round, biconvex, red film-coated tablets, debossed with the “Bayer cross” on one side and “200” on the other side |
| Imprint code / Engraving / Debossment | Debossed with the “Bayer cross” on one side and “200” on the other side |
| Score | No Score |
| Color | Red |
| Shape | Round |
| Dimension | 10 mm |
| Mfg by | Bayer HealthCare AG (EU) |
| Mfg for | Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc (US) |
| Marketed by | - |
| Distributed by | - |
| Application No. | Prod No | Patent No | Patent Expiration | Drug Substance Claim | Drug Product Claim | Patent Use Code | Delist Requested | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N021923 | 1 | 7235576 | January 12, 2020 | Y | Y | - | - | Download |
| N021923 | 1 | 7351834 | January 12, 2020 | Y | - | - | - | Download |
| N021923 | 1 | 7897623 | January 12, 2020 | - | Y | - | - | Download |
| N021923 | 1 | 8124630 | January 12, 2020 | - | - | U - 1459 | - | Download |
| N021923 | 1 | 8618141 | February 11, 2023 | - | - | U - 1480 | - | Download |
| N021923 | 1 | 8841330 | January 12, 2020 | - | - | U - 1696 | - | Download |
| N021923 | 1 | 8877933 | December 24, 2027 | Y | Y | U - 1624 | - | Download |
| USP Apparatus | Speed (RPMs) | Medium | Volume (mL) | Recommended Sampling Times (minutes) | Date Updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II (Paddle) | 75 | 0.1 M HCl with 1% SDS | 900 | 5, 10, 15, 20 and 30 | June 10, 2009 |
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| FDA label | Download |
| FDA chemistry review | Download |
| FDA Pharmacology Review(s) | Download |
| FDA Clinical Pharmacology Biopharmaceutics Review(s) | Download |
| FDA BE Recommendation | Download |
| European Public Assessment Report | Download |
| Territory | Brand name / Generic company name | Link |
|---|---|---|
| EU | Nexavar | Download |
| UK | Nexavar | Download |
| US | NEXAVAR | Download |
| Sorafenib tosylate (274 mg) equivalent to 200 mg of sorafenib. Product manufactured in Germany (US). Date of first authorisation in EU: 19 July 2006. I - 677 Exclusivity Expiration on Nov 22, 2016. |
| www.accessdata.fda.gov, www.drugbank.ca, www.ema.europa.eu, www.medicines.org.uk, dailymed.nlm.nih.gov |
