| Active Ingredient | SITAGLIPTIN PHOSPHATE |
|---|
| Drug Name | FDA Application No. | Company | Dosage Form;Route | Strength | RLD Strength | Original Approval or Tentative Approval Date |
Exclusivity Expiration (NCE) |
Exclusivity Expiration (ODE) |
Chemical Type |
Review Classification |
Marketing Status |
TE Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JANUVIA | (NDA) 021995 | MERCK SHARP DOHME | TABLET;ORAL | EQ 25MG BASE EQ 50MG BASE EQ 100MG BASE | EQ 100MG BASE | October 16, 2006 | "-" | "-" | 1 New molecular entity (NME) | S Standard review drug | Prescription | None |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Structural Formula |
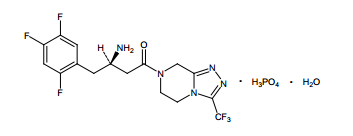 |
| Chemical Name | 7-[(3R)-3-amino-1-oxo-4-(2,4,5trifluorophenyl)butyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazine phosphate (1:1) monohydrate |
| CAS No | 486460-32-6 |
| Molecular Formula | C16H15F6N5O•H3PO4•H2O |
| Molecular Weight | 523.32 |
| Appearance | white to off-white, crystalline, non-hygroscopic powder |
| Solubility | Soluble in N,N-dimethyl formamide; slightly soluble in methanol; very slightly soluble in ethanol, acetone, and acetonitrile; and insoluble in isopropanol and isopropyl acetate. |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water (Predicted: 0.034 mg/mL) |
| Polymorphism | - |
| pKa (Strongest Acidic) | - |
| pKa (Strongest Basic) | 8.78 (Predicted) |
| Log P | 1.5 |
| Identification | IR |
| Degradation | - |
| Hygroscopic | Non-hygroscopic |
| Photostability study | The active substance is not susceptible to degradation under the influence of light |
| Melting Point | - |
| BCS Class | - |
| Manufacture of API | Sitagliptin is synthesised in two reactions steps and purified by crystallisation. |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Indications and Usage | JANUVIA is a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Important Limitations of Use: • JANUVIA should not be used in patients with type 1 diabetes or for the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis. • JANUVIA has not been studied in patients with a history of pancreatitis. |
| Dosage and Administration |
The recommended dose of JANUVIA is 100 mg once daily. JANUVIA can be taken with or without food. Dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with moderate or severe renal insufficiency or end-stage renal disease Dosage Adjustment in Patients With Moderate, Severe and End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) 50 mg once daily: Moderate CrCl ≥30 to <50 mL/min ~Serum Cr levels [mg/dL] Men: >1.7– ≤3.0; Women: >1.5– ≤2.5 25 mg once daily: Severe and ESRD CrCl <30 mL/min ~Serum Cr levels [mg/dL] Men: >3.0; Women: >2.5; or on dialysis |
| Mechanism of action |
Sitagliptin is a DPP-4 inhibitor, which is believed to exert its actions in patients with type 2 diabetes by slowing the inactivation of incretin hormones. Concentrations of the active intact hormones are increased by JANUVIA, thereby increasing and prolonging the action of these hormones. Incretin hormones, including glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), are released by the intestine throughout the day, and levels are increased in response to a meal. These hormones are rapidly inactivated by the enzyme, DPP-4. The incretins are part of an endogenous system involved in the physiologic regulation of glucose homeostasis. When blood glucose concentrations are normal or elevated, GLP-1 and GIP increase insulin synthesis and release from pancreatic beta cells by intracellular signaling pathways involving cyclic AMP. GLP-1 also lowers glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha cells, leading to reduced hepatic glucose production. By increasing and prolonging active incretin levels, JANUVIA increases insulin release and decreases glucagon levels in the circulation in a glucose-dependent manner. Sitagliptin demonstrates selectivity for DPP-4 and does not inhibit DPP-8 or DPP-9 activity in vitro at concentrations approximating those from therapeutic doses. |
| Absorption | The pharmacokinetics of sitagliptin has been extensively characterized in healthy subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes. After oral administration of a 100 mg dose to healthy subjects, sitagliptin was rapidly absorbed, with peak plasma concentrations (median Tmax) occurring 1 to 4 hours postdose. Plasma AUC of sitagliptin increased in a dose-proportional manner. Following a single oral 100 mg dose to healthy volunteers, mean plasma AUC of sitagliptin was 8.52 µM•hr, Cmax was 950 nM, and apparent terminal half-life (t1/2) was 12.4 hours. Plasma AUC of sitagliptin increased approximately 14% following 100 mg doses at steady-state compared to the first dose. The intra-subject and inter-subject coefficients of variation for sitagliptin AUC were small (5.8% and 15.1%). The pharmacokinetics of sitagliptin was generally similar in healthy subjects and in patients with type 2 diabetes. |
| Food Effect | Because coadministration of a high-fat meal with JANUVIA had no effect on the pharmacokinetics, JANUVIA may be administered with or without food. |
| Distribution | The mean volume of distribution at steady state following a single 100 mg intravenous dose of sitagliptin to healthy subjects is approximately 198 liters. The fraction of sitagliptin reversibly bound to plasma proteins is low (38%). |
| Metabolism | Approximately 79% of sitagliptin is excreted unchanged in the urine with metabolism being a minor pathway of elimination. Following a [14C]sitagliptin oral dose, approximately 16% of the radioactivity was excreted as metabolites of sitagliptin. Six metabolites were detected at trace levels and are not expected to contribute to the plasma DPP-4 inhibitory activity of sitagliptin. In vitro studies indicated that the primary enzyme responsible for the limited metabolism of sitagliptin was CYP3A4, with contribution from CYP2C8. Excretion Following administration of an oral [14C]sitagliptin dose to healthy subjects, approximately 100% of the administered radioactivity was eliminated in feces (13%) or urine (87%) within one week of dosing. The apparent terminal t1/2 following a 100 mg oral dose of sitagliptin was approximately 12.4 hours and renal clearance was approximately 350 mL/min. |
| Elimination | Elimination of sitagliptin occurs primarily via renal excretion and involves active tubular secretion. Sitagliptin is a substrate for human organic anion transporter-3 (hOAT-3), which may be involved in the renal elimination of sitagliptin. The clinical relevance of hOAT-3 in sitagliptin transport has not been established. Sitagliptin is also a substrate of p-glycoprotein, which may also be involved in mediating the renal elimination of sitagliptin. However, cyclosporine, a p-glycoprotein inhibitor, did not reduce the renal clearance of sitagliptin |
| Peak plasma time (Tmax) | 1 to 4 hours |
| Half life | 12.4 hours |
| Bioavailability | The absolute bioavailability of sitagliptin is approximately 87%. |
| Age, gender | No dosage adjustment is necessary based on gender. Gender had no clinically meaningful effect on the pharmacokinetics of sitagliptin based on a composite analysis of Phase I pharmacokinetic data and on a population pharmacokinetic analysis of Phase I and Phase II data. |
| DMF | Status | Type | Submit Date | Holder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | - | - | |
| 23864 | A | II | June 3, 2010 | MSN PHARMACHEM PRIVATE LTD |
| 24067 | A | II | August 16, 2010 | MYLAN LABORATORIES LTD |
| 24148 | A | II | September 9, 2010 | TEVA PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRIES LTD |
| 24199 | A | II | October 9, 2010 | SUN PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRIES LTD |
| 24266 | A | II | October 8, 2010 | APOTEX PHARMACHEM INC |
| 25773 | A | II | March 29, 2012 | GLENMARK PHARMACEUTICALS LTD |
| 25867 | A | II | March 2, 2012 | TEVA PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRIES LTD |
| 26425 | A | II | September 11, 2012 | ZHEJIANG APELOA JIAYUAN PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD |
| 26495 | A | II | September 26, 2012 | SICHUAN XIELI PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD |
| 26783 | A | II | March 11, 2013 | GLENMARK PHARMACEUTICALS LTD |
| 26885 | A | II | March 27, 2013 | GLENMARK PHARMACEUTICALS LTD |
| 26974 | A | II | April 5, 2013 | MSN PHARMACHEM PRIVATE LTD |
| 27084 | A | II | May 27, 2013 | WOCKHARDT BIO AG |
| 28325 | A | II | May 29, 2014 | BEIJING HUIKANG BOYUAN CHEMICAL TECH CO LTD |
| 28344 | A | II | June 17, 2015 | ZHEJIANG CHANGMING PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD |
| 28654 | A | II | October 10, 2014 | CADILA HEALTHCARE LTD |
| 28908 | A | II | May 15, 2015 | SINTENOVO SA DE CV |
| 29226 | A | II | March 27, 2015 | VIWIT PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD |
| 29508 | A | II | June 19, 2015 | ZHEJIANG APELOA JIAYUAN PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD |
| 30082 | A | II | December 22, 2015 | JUBILANT GENERICS LTD |
| 30170 | A | II | January 19, 2016 | HEC PHARM CO LTD |
| 30181 | A | II | December 30, 2015 | VIWIT PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD |
| 30757 | A | II | November 9, 2016 | MACLEODS PHARMACEUTICALS LTD |
| 30857 | A | II | September 22, 2016 | HONOUR LAB LTD |
| 30974 | A | II | October 12, 2016 | HARMAN FINOCHEM LTD |
| 31579 | A | II | March 17, 2017 | HIKAL LTD |
| x | - | - | - |
| Parameters | Details | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | EQ 25MG BASE | EQ 50MG BASE | EQ 100MG BASE | |
| Excipients used | Microcrystalline cellulose, anhydrous dibasic calcium phosphate, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, and sodium stearyl fumarate | |||
| Composition of coating material | Polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, talc, titanium dioxide, red iron oxide, and yellow iron oxide | |||
| Composition of caspule shell | - | |||
| Pharmaceutical Development |
Each film-coated tablet of JANUVIA contains 32.13, 64.25, or 128.5 mg of sitagliptin phosphate monohydrate, which is equivalent to 25, 50, or 100 mg, respectively All information regarding the choice of the active substance and the excipients are sufficiently justified. Sitagliptin tablets were developed in four tablet strengths (25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg and 200 mg). The main aim of the applicant was to develop a formulation that would rapidly release the active substance, that would behave as much as possible as an oral solution upon dosing and would provide a consistent bioavailability. In this context, the excipients have been chosen not only to achieve these aims but also to ensure the chemical stability. A direct compression manufacturing process was selected based on its inherent simplicity and demonstrated ability to produce high quality tablets reproducibly. Results of formulation and process development studies demonstrate that the tablet formulation and the manufacturing process are robust and under control. |
|||
| Manufacture of the product |
The proposed commercial manufacturing process involves standard technology using standard manufacturing processes such as blending, lubrication, direct compression and film-coating unit operations. Furthermore, the equipment used is commonly available in the pharmaceutical industry. It was demonstrated that there are no critical steps in the manufacturing process. |
|||
| Tablet / Capsule Image |

|

|

|
|
| Appearance | Pink, round, film-coated tablets with “221” on one side | Light beige, round, film-coated tablets with “112” on one side | Beige, round, film-coated tablets with “277” on one side | |
| Imprint code / Engraving / Debossment | “221” on one side plain on other side | “112” on one side plain on other side | “277” on one side plain on other side | |
| Score | No score | No score | No score | |
| Color | Pink | Light beige | Beige | |
| Shape | Round | Round | Round | |
| Dimension | - | 8mm | 10mm | |
| Mfg by | - | |||
| Mfg for | - | |||
| Marketed by | Merck Sharp & Dohme Ltd. (EU/UK) | |||
| Distributed by | Merck & Co. (US) | |||
| Application No. | Prod No | Patent No | Patent Expiration | Drug Substance Claim | Drug Product Claim | Patent Use Code | Delist Requested | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N021995 | 1 | 6699871 | July 26, 2022 | Y | Y | U - 774 | - | Download |
| N021995 | 1 | 7125873 | July 26, 2022 | - | - | U - 775 | - | Download |
| N021995 | 1 | 7125873 | July 26, 2022 | - | - | U - 775 | - | Download |
| N021995 | 1 | 7125873 | July 26, 2022 | - | - | U - 775 | - | Download |
| N021995 | 1 | 7125873 | July 26, 2022 | - | - | U - 775 | - | Download |
| N021995 | 1 | 7326708 | November 24, 2026 | Y | Y | U - 802 | - | Download |
| USP Apparatus | Speed (RPMs) | Medium | Volume (mL) | Recommended Sampling Times (minutes) | Date Updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I (Basket) | 100 | Water | 900 | 5, 10, 15, 20 and 30 | July 1, 2010 |
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| FDA label | Download |
| FDA chemistry review | Download |
| FDA Pharmacology Review(s) | Download |
| FDA Clinical Pharmacology Biopharmaceutics Review(s) | Download |
| FDA BE Recommendation | Download |
| European Public Assessment Report | Download |
| Territory | Brand name / Generic company name | Link |
|---|---|---|
| EU | Januvia | Download |
| UK | Januvia | Download |
| US | APOTEX INC (ANDA # 202425)*- Tentative Approval | |
| US | JANUVIA | Download |
| US | MYLAN PHARMS INC (ANDA # 202473)*- Tentative Approval | |
| US | SANDOZ INC (ANDA # 202387)*- Tentative Approval | |
| US | SUN PHARMA GLOBAL (ANDA # 202423)*- Tentative Approval | |
| US | TEVA PHARMS USA (ANDA # 202487)*- Tentative Approval | |
| US | WATSON LABS INC (ANDA # 202327)*- Tentative Approval |
| Date of first authorisation in EU/UK: 21 March 2007 |
| www.accessdata.fda.gov, www.drugbank.ca, www.ema.europa.eu, www.medicines.org.uk, dailymed.nlm.nih.gov |
