| Active Ingredient | SILODOSIN |
|---|
| Drug Name | FDA Application No. | Company | Dosage Form;Route | Strength | RLD Strength | Original Approval or Tentative Approval Date |
Exclusivity Expiration (NCE) |
Exclusivity Expiration (ODE) |
Chemical Type |
Review Classification |
Marketing Status |
TE Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAPAFLO | (NDA) 022206 | ACTAVIS LABS UT INC | CAPSULE;ORAL | 4MG, 8MG | 4MG (RS), 8MG | October 8, 2008 | - | - | 1 New molecular entity (NME) | S Standard review drug | Prescription | None |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Structural Formula |
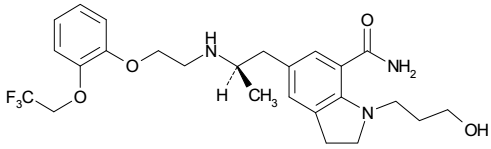 |
| Chemical Name | 1-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-5-[(2R)-2-({2-[2-(2,2,2trifluoroethoxy)phenoxy]ethyl}amino)propyl]-2,3-dihydro-1H-indole-7-carboxamide |
| CAS No | 160970-54-7 |
| Molecular Formula | C25H32F3N3O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 495.53 |
| Appearance | a white to pale yellowish white powder and odorless |
| Solubility | It is very soluble in acetic acid, freely soluble in methanol, N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), and ethanol, sparingly soluble in 1-octanol, and very slightly soluble in water. It was verified that this active substance is soluble in various buffers at acidic pH but very slightly at alkaline pH. |
| Water Solubility | 0.0111 mg/mL (Predicted) |
| Polymorphism | Silodosin can exist in three polymorphic forms. The forms can be differentiated by IR, PXRD and solid-state 13C-NMR. A well defined polymorph was selected to manufacture the finished product. |
| pKa (Strongest Acidic) | 14.87 (Predicted) |
| pKa (Strongest Basic) | 9.66 (Predicted) |
| Log P | 2.96 (Predicted) |
| Identification | IR, fluoride, mp |
| Degradation | - |
| Hygroscopic | non hygroscopic |
| Photostability study | - |
| Melting Point | 105 - 109°C |
| BCS Class | - |
| Manufacture of API | Silodosin is synthesised in five reactions steps. The active substance is manufactured by two manufacturers. However, it is important to underline that the synthetic process and controls on the active substance are the same for the two sources of silodosin. The manufacturing process has been adequately described. Critical parameters have been identified and adequate in-process controls included. Specifications for starting materials, reagents, and solvents have been provided. Adequate control of critical steps and intermediates has been presented. The active substance is purified by recrystallisation and the crystallised active substance is finally milled. |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Indications and Usage | RAPAFLO, a selective alpha-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist, is indicated for the treatment of the signs and symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). RAPAFLO is not indicated for the treatment of hypertension. |
| Dosage and Administration |
The recommended dose is 8 mg orally once daily with a meal. Patients who have difficulty swallowing pills and capsules may carefully open the RAPAFLO capsule and sprinkle the powder inside on a tablespoonful of applesauce. The applesauce should be swallowed immediately (within 5 minutes) without chewing and followed with an 8 oz glass of cool water to ensure complete swallowing of the powder. The applesauce used should not be hot, and it should be soft enough to be swallowed without chewing. Any powder/applesauce mixture should be used immediately (within 5 minutes) and not stored for future use. Subdividing the contents of a RAPAFLO capsule is not recommended. |
| Mechanism of action |
Silodosin is a selective antagonist of post-synaptic alpha-1 adrenoreceptors, which are located in the human prostate, bladder base, bladder neck, prostatic capsule, and prostatic urethra. Blockade of these alpha-1 adrenoreceptors can cause smooth muscle in these tissues to relax, resulting in an improvement in urine flow and a reduction in BPH symptoms. An in vitro study examining binding affinity of silodosin to the three subtypes of the alpha-1 adrenoreceptors (alpha-1A, alpha-1B, and alpha-1D) was conducted. The results of the study demonstrated that silodosin binds with high affinity to the alpha-1A subtype. |
| Absorption | The pharmacokinetics of silodosin have been evaluated in adult male subjects with doses ranging from 0.1 mg to 24 mg per day. The pharmacokinetics of silodosin are linear throughout this dosage range. Cmax and AUC were 61.6 ± 27.54 ng/mL and 373.4 ± 164.94 ng•hr/mL. |
| Food Effect |
The maximum effect of food (i.e., co-administration with a high fat, high calorie meal) on the PK of silodosin was not evaluated. The effect of a moderate fat, moderate calorie meal was variable and decreased silodosin Cmax by approximately 18 - 43% and AUC by 4 - 49% across three different studies. In a single-center, open-label, single-dose, randomized, two-period crossover study in twenty healthy male subjects age 21 to 43 years under fed conditions, a study was conducted to evaluate the relative bioavailability of the contents of an 8 mg capsule (size #1) of silodosin sprinkled on applesauce compared to the product administered as an intact capsule. Based on AUC0-24 and Cmax, silodosin administered by sprinkling the contents of a RAPAFLO capsule onto a tablespoonful of applesauce was found to be bioequivalent to administering the capsule whole. |
| Distribution | Silodosin has an apparent volume of distribution of 49.5 L and is approximately 97% protein bound. |
| Metabolism | Silodosin undergoes extensive metabolism through glucuronidation, alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase, and cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) pathways. The main metabolite of silodosin is a glucuronide conjugate (KMD-3213G) that is formed via direct conjugation of silodosin by UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 2B7 (UGT2B7). Co-administration with inhibitors of UGT2B7 (e.g., probenecid, valproic acid, fluconazole) may potentially increase exposure to silodosin. KMD-3213G, which has been shown in vitro to be active, has an extended half-life (approximately 24 hours) and reaches plasma exposure (AUC) approximately four times greater than that of silodosin. The second major metabolite (KMD-3293) is formed via alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenases and reaches plasma exposures similar to that of silodosin. KMD-3293 is not expected to contribute significantly to the overall pharmacologic activity of RAPAFLO. |
| Elimination | Following oral administration of 14C-labeled silodosin, the recovery of radioactivity after 10 days was approximately 33.5% in urine and 54.9% in feces. After intravenous administration, the plasma clearance of silodosin was approximately 10 L/hour. |
| Peak plasma time (Tmax) | 2.6 ± 0.90 hours |
| Half life | 13.3 ± 8.07 hours |
| Bioavailability | The absolute bioavailability is approximately 32% |
| Age, gender |
No clinical studies specifically investigating the effects of race have been performed. In a study comparing 12 geriatric males (mean age 69 years) and 9 young males (mean age 24 years), the exposure (AUC) and elimination half-life of silodosin were approximately 15% and 20%, respectively, greater in geriatric than young subjects. No difference in the Cmax of silodosin was observed. RAPAFLO has not been evaluated in patients less than 18 years of age. |
| DMF | Status | Type | Submit Date | Holder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13030 | A | II | June 18, 1998 | KISSEI PHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD |
| 26251 | A | II | October 9, 2012 | CADILA HEALTHCARE LTD |
| 26423 | A | II | September 14, 2012 | HETERO DRUGS LTD |
| 26459 | A | II | September 21, 2012 | SANDOZ PRIVATE LTD |
| 26957 | A | II | June 4, 2013 | MSN LABORATORIES PRIVATE LTD |
| 27082 | A | II | April 20, 2013 | ALP PHARM BEIJING CO LTD |
| 29518 | A | II | July 15, 2015 | ZHEJIANG HUAHAI PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD |
| 29659 | A | II | September 4, 2015 | ALEMBIC PHARMACEUTICALS LTD |
| 29777 | A | II | May 31, 2016 | JOHNSON MATTHEY PHARMA SERVICES |
| 31029 | A | II | November 15, 2016 | TORRENT PHARMACEUTICALS LTD |
| 31316 | A | II | January 19, 2017 | AUROBINDO PHARMA LTD |
| 31359 | A | II | May 2, 2017 | MACLEODS PHARMACEUTICALS LTD |
| Parameters | Details | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | 4MG | 8MG | |
| Excipients used | D-mannitol, magnesium stearate, pregelatinized starch, and sodium lauryl sulfate | ||
| Composition of coating material | - | ||
| Composition of caspule shell |
Size #3 hard gelatin capsules contain gelatin and titanium dioxide. The capsules are printed with edible ink containing yellow iron oxide. |
Size #1 hard gelatin capsules contain gelatin and titanium dioxide. The capsules are printed with edible ink containing FD&C Blue No. 1 Aluminum Lake and yellow iron oxide |
|
| Pharmaceutical Development |
The main aim of the formulation development was to obtain a composition with good homogeneity and performance (disintegration and dissolution) characteristics. The manufacturer developed silodosin 8 mg capsules with a content which is proportionally similar in its active and inactive ingredients to the 4 mg capsules already marketed in Japan by Kissei and utilised also by Watson. It was noted that there were no changes in the manufacture of the blend of the two strengths. Comparative dissolution profiles were obtained for the 4 mg and 8 mg capsules using three different dissolution media pH 1.2, 4.5, 6.8. |
||
| Manufacture of the product | The proposed commercial manufacturing process involves standard technology using standard manufacturing processes such as mixing, granulation, sieving and capsule filling. | ||
| Tablet / Capsule Image |
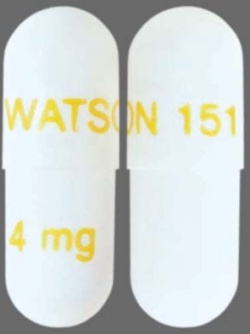
|
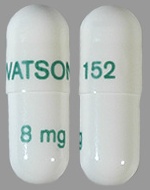
|
|
| Appearance | white, opaque, hard #3 gelatin capsules imprinted with “WATSON 151” in gold on the cap and “4 mg” in gold on the body | white, opaque, hard #1 gelatin capsules imprinted with “WATSON 152” in green on the cap and “8 mg” in green on the body | |
| Imprint code / Engraving / Debossment | imprinted with “WATSON 151” in gold on the cap and “4 mg” in gold on the body | imprinted with “WATSON 152” in green on the cap and “8 mg” in green on the body | |
| Score | no score | no score | |
| Color | White opaque | White opaque | |
| Shape | Capsule | Capsule | |
| Dimension | Size 3 | Size 1 (19mm) | |
| Mfg by | Watson Laboratories, Inc. (US), Recordati Ltd. (EU) | ||
| Mfg for | - | ||
| Marketed by | Recordati Ireland Ltd. (EU) | ||
| Distributed by | Watson Laboratories, Inc. (US) | ||
| Application No. | Prod No | Patent No | Patent Expiration | Drug Substance Claim | Drug Product Claim | Patent Use Code | Delist Requested | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N022206 | 1 | 5387603 | December 1, 2018 | Y | Y | - | - | Download |
| USP Apparatus | Speed (RPMs) | Medium | Volume (mL) | Recommended Sampling Times (minutes) | Date Updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II (Paddle) with sinker | 50 | 0.1 N HCl | 900 | 5, 10, 15, 20 and 30 | June 7, 2012 |
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| FDA label | Download |
| FDA chemistry review | |
| FDA Pharmacology Review(s) | Download |
| FDA Clinical Pharmacology Biopharmaceutics Review(s) | Download |
| FDA BE Recommendation | Download |
| European Public Assessment Report | Download |
| Territory | Brand name / Generic company name | Link |
|---|---|---|
| EU | UROREC | Download |
| UK | - | |
| US | LUPIN PHARMS (ANDA #206541)* | |
| US | RAPAFLO | Download |
| US | SANDOZ INC (ANDA #204726)* | Download |
| - |
| www.accessdata.fda.gov, www.drugbank.ca, www.ema.europa.eu, www.medicines.org.uk, dailymed.nlm.nih.gov, www.drug.com |
