| Active Ingredient | RIVAROXABAN |
|---|
| Drug Name | FDA Application No. | Company | Dosage Form;Route | Strength | RLD Strength | Original Approval or Tentative Approval Date |
Exclusivity Expiration (NCE) |
Exclusivity Expiration (ODE) |
Chemical Type |
Review Classification |
Marketing Status |
TE Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XARELTO | (NDA) 022406 | JANSSEN PHARMS | TABLET;ORAL | 10MG, 15MG, 20MG | 10MG, 15MG, 20MG (RS) | July 1, 2011 | - | - | 1 New molecular entity (NME) | S Standard review drug | Prescription | None |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Structural Formula |
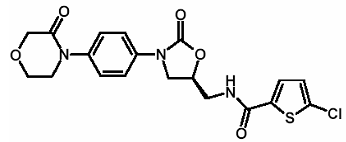 |
| Chemical Name | 5-Chloro-N-({(5S)-2-oxo-3-[4-(3-oxo-4-morpholinyl)phenyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-5-yl}methyl)-2-thiophenecarboxamide |
| CAS No | 366789-02-8 |
| Molecular Formula | C19H18ClN3O5S |
| Molecular Weight | 435.89 |
| Appearance | white to yellowish powder |
| Solubility | slightlysoluble in organic solvents (e.g., acetone, polyethylene glycol 400) and is practically insoluble in water and aqueous media with pH 1 – 9 (pH-independent 5 - 7 mg/L are soluble at 25 °C). |
| Water Solubility | 0.01 mg/mL (Predicted) |
| Polymorphism | Rivaroxaban crystallizes in three polymorphs. Polymorph I is the thermodynamically stable one and has been used in all tablet formulations during clinical development and will be used in the commercial product. The identity of polymorph I is routinely controlled by Raman spectroscopy at release. |
| pKa (Strongest Acidic) | 13.6 (Predicted) |
| pKa (Strongest Basic) | (Predicted) -1.6 |
| Log P | 1.5 |
| Identification | IR, high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) |
| Degradation | The results of stress conditions (thermal, hydrolytic and oxidative stress) studies show that rivaroxaban is a very stable substance with regards to thermal conditions and sufficiently stable with regards to hydrolytic stress. |
| Hygroscopic | non-hygroscopic |
| Photostability study | Photo stable |
| Melting Point | - |
| BCS Class | II |
| Manufacture of API | Rivaroxaban is synthesised using a five-step synthetic process using 4-(4-nitrophenyl)-3-morpholinone as a starting material. Three key intermediates must be synthesised, which are then used in the reaction to form the active substance. After re-crystallization of rivaroxaban crude, the material is micronised. |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Indications and Usage | XARELTO is indicated to reduce the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. There are limited data on the relative effectiveness of XARELTO and warfarin in reducing the risk of stroke and systemic embolism when warfarin therapy is well-controlled. XARELTO is indicated for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). XARELTO is indicated for the treatment of pulmonaryembolism (PE). XARELTO is indicated for the reduction in the risk of recurrence of deep vein thrombosis and of pulmonaryembolism following initial 6 months treatment for DVT and/or PE. XARELTO is indicated for the prophylaxis of DVT, which maylead to PE in patients undergoing knee or hip replacement surgery. |
| Dosage and Administration |
In Reduction in Risk of Stroke in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation, 20 mg once daily with the evening meal and 15 mg once daily with the evening meal are recommended with CrCl >50 mL/min and CrCl 15 to 50 mL/min respectively. In treatment of DVT and treatment of PE, 15 mg twice daily with food, for first 21 days is recommended and after 21 days, 20 mg once daily with food, for remaining treatment. In Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of DVT and of PE, 20 mg once daily with food is recommended. |
| Mechanism of action | XARELTO is a selective inhibitor of FXa. It does not require a cofactor (such as Anti-thrombin III) for activity. Rivaroxaban inhibits free FXa and prothrombinase activity. Rivaroxaban has no direct effect on platelet aggregation, but indirectly inhibits platelet aggregation induced by thrombin. By inhibiting FXa, rivaroxaban decreases thrombin generation. |
| Absorption |
The absolute bioavailabilityof rivaroxaban is dose-dependent. For the 10 mg dose, it is estimated to be 80% to 100% and is not affected byfood. XARELTO 10 mg tablets can be taken with or without food. For the 20 mg dose in the fasted state, the absolute bioavailability is approximately 66%. Coadministration of XARELTO with food increases the bioavailabilityof the 20 mg dose (mean AUC and Cmax increasing by39% and 76% respectively with food). XARELTO 15 mg and 20 mg tablets should be taken with food. The maximum concentrations (Cmax) of rivaroxaban appear 2 to 4 hours after tablet intake. The pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban were not affected bydrugs altering gastric pH. Coadministration of XARELTO (30 mg single dose) with the H2-receptor antagonist ranitidine (150 mg twice daily), the antacid aluminum hydroxide/magnesium hydroxide (10 mL) or XARELTO (20 mg single dose) with the PPIomeprazole (40 mg once daily) did not show an effect on the bioavailabilityand exposure of rivaroxaban. Absorption of rivaroxaban is dependent on the site of drug release in the GI tract. A 29% and 56% decrease in AUC and Cmax compared to tablet was reported when rivaroxaban granulate is released in the proximal small intestine. Exposure is further reduced when drug is released in the distal small intestine, or ascending colon. Avoid administration of rivaroxaban distal to the stomach which can result in reduced absorption and related drug exposure. |
| Food Effect | In a study with 44 healthy subjects, both mean AUC and Cmax values for 20 mg rivaroxaban administered orally as a crushed tablet mixed in applesauce were comparable to that after the whole tablet. However, for the crushed tablet suspended in water and administered via an NG tube followed by a liquid meal, only mean AUC was comparable to that after the whole tablet, and Cmax was 18% lower. |
| Distribution | Plasma protein binding of rivaroxaban in human plasma is approximately 92% to 95%, with albumin being the main binding component. The steady-state volume of distribution in healthy subjects is approximately 50 L. |
| Metabolism | Approximately 51% of an orally administered [14C]-rivaroxaban dose was recovered as inactive metabolites in urine (30%) and feces (21%). Oxidative degradation catalyzed by CYP3A4/5 and CYP2J2 and hydrolysis are the major sites of biotransformation. Unchanged rivaroxaban was the predominant moiety in plasma with no major or active circulating metabolites. |
| Elimination |
Following oral administration, approximatelyone-third of the absorbed dose is excreted unchanged in the urine, with the remaining two-thirds excreted as inactive metabolites in both the urine and feces. In a Phase 1 study, following the administration of a [14C]-rivaroxaban dose, 66% of the radioactive dose was recovered in urine (36% as unchanged drug) and 28% was recovered in feces (7% as unchanged drug). Unchanged drug is excreted into urine, mainly via active tubular secretion and to a lesser extent via glomerular filtration (approximate 5:1 ratio). Rivaroxaban is a substrate of the efflux transporter proteins P-gp and ABCG2 (also abbreviated Bcrp). Rivaroxaban’s affinityfor influx transporter proteins is unknown. Rivaroxaban is a low-clearance drug, with a systemic clearance of approximately10 L/hr in healthyvolunteers following intravenous administration. The terminal elimination half-life of rivaroxaban is 5 to 9 hours in healthy subjects aged 20 to 45 years. |
| Peak plasma time (Tmax) | 2 to 4 hours |
| Half life | 5 to 9 hours |
| Bioavailability | 66% (Fasted) |
| Age, gender |
Gender did not influence the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of XARELTO. In clinical studies, elderlysubjects exhibited higher rivaroxaban plasma concentrations than younger subjects with mean AUC values being approximately 50% higher, mainly due to reduced (apparent) total bodyand renal clearance. Age related changes in renal function may playa role in this age effect. The terminal elimination half-life is 11 to 13 hours in the elderly. |
| DMF | Status | Type | Submit Date | Holder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21581 | A | II | July 23, 2008 | BAYER PHARMA AG |
| 27661 | A | II | October 21, 2013 | ZAKLADY FARMACEUTYCZNE POLPHARMA SA |
| 27807 | A | II | December 31, 2013 | MSN LABORATORIES PRIVATE LTD |
| 28056 | A | II | March 28, 2014 | ALEMBIC PHARMACEUTICALS LTD |
| 28121 | A | II | March 31, 2014 | DR REDDYS LABORATORIES LTD |
| 28199 | A | II | April 10, 2014 | VIWIT PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD |
| 28323 | A | II | June 5, 2014 | ZHEJIANG HUAHAI PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD |
| 28786 | A | II | January 8, 2015 | HEC PHARM CO LTD |
| 28790 | A | II | October 30, 2014 | OPTIMUS DRUGS PRIVATE LTD {"4-(4-AMINOPHENYL) MORPHOLIN-3-ONE [RIVAROXABAN INTERMEDIATE, (PROCESS-1)]"} |
| 28798 | A | II | January 21, 2015 | LUPIN LTD |
| 28807 | A | II | June 11, 2014 | SYMED LABS LTD |
| 28816 | A | II | March 6, 2015 | TARO PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRIES LTD |
| 28864 | A | II | January 16, 2015 | GLENMARK PHARMACEUTICALS LTD |
| 28916 | A | II | December 23, 2014 | MEDICHEM MANUFACTURING MALTA LTD |
| 28922 | A | II | December 31, 2014 | APOTEX PHARMACHEM INDIA PVT LTD |
| 28927 | A | II | December 10, 2014 | MEGAFINE PHARMA P LTD |
| 28993 | A | II | January 23, 2015 | INTERQUIM SA |
| 29048 | A | II | February 5, 2015 | AUROBINDO PHARMA LTD |
| 29066 | A | II | March 18, 2015 | RAKS PHARMA PVT LTD |
| 29439 | A | II | May 18, 2015 | ZHEJIANG SUPOR PHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD |
| 30403 | A | II | March 31, 2016 | PIRAMAL ENTERPRISES LTD |
| Parameters | Details | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | 10MG | 15MG | 20MG | |
| Excipients used | croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium lauryl sulfate | croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate (25.40MG), magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium lauryl sulfate | croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate (22.90MG), magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium lauryl sulfate | |
| Composition of coating material | Opadry Pink containing ferric oxide red, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol 3350, and titanium dioxide, and | Opadry Red containing ferric oxide red, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol 3350, and titanium dioxide | Opadry II Dark Red, containing ferric oxide red, polyethylene glycol 3350, polyvinyl alcohol (partially hydrolyzed), talc, and titanium dioxide | |
| Composition of caspule shell | - | |||
| Pharmaceutical Development |
The development objective was to provide a small size immediate release tablet formulation of rivaroxaban. The active substance is practically insoluble in water and it has a high permeability as shown by the results of a validated Caco-2 assay. Therefore it could be classified as a Class II substance in the Biopharmaceutics Classification System (low solubility, high permeability). The problem of the low solubility of the active substance is addressed by reducing its particle size with micronisation to increase the particle surface area and thus facilitate dissolution. Dissolution profiles obtained on micronised batches of rivaroxaban were compared to non-micronised (crystalline) ones and the results support the need for micronisation of the active substance. When comparing the dissolution kinetics of micronised active substance within the specified limits of particle size distribution (e.g. X90 < 15 µm), significant differences of dissolution kinetics can not be observed. For the formulation development well-known standard excipients that are often used in immediate release tablet formulations were employed. Microcrystalline cellulose and lactose monohydrate act as fillers, croscarmellose sodium as a disintegrant, hypromellose 5 cp as a binder, sodium laurilsulfate as a wetting agent and magnesium stearate as a lubricant. Lactose monohydrate is produced from milk from healthy animals in the same conditions as milk collected for human consumption and the magnesium stearate used is of vegetable origin A standard fluid bed granulation process has been developed, followed by final mixing, tabletting and filmcoating. The impact of manufacturing process parameters on target properties of the final dosage form, such as tablet hardness, disintegration, dissolution, content uniformity and stability has been investigated during development and scale-up and appropriate operating ranges have been set to ensure that the finished product is of the intended quality. The tablet dissolution rate is a critical quality attribute of the product and is influenced by active substance particle size. Therefore a discriminating dissolution test method has been developed for the release of the product. The dissolution test is performed in an acetate buffer of pH 4.5. Under these conditions the tablets show nearly complete dissolution (> 80 %) within 30 minutes. The aspects that were challenged included the influence of disintegrant; granulation time; blending time; addition of wetting agent; accelerated stability testing and compression force. In all cases the discriminatory power of the dissolution test was sufficiently demonstrated. The relevance of the specifications set for the active substance particle size distribution has been confirmed by in vivo studies in dogs showing that the oral absorption is independent on API particle size after administration of tablets manufactured with API within the proposed specification limits. |
|||
| Manufacture of the product | The manufacturing process consists of the following main steps: fluidised-bed granulation, mixing, tabletting and film-coating. All critical process parameters have been identified and controlled by appropriate in process controls. | |||
| Tablet / Capsule Image |

|

|
|
|
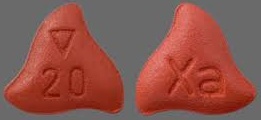
| Appearance | Round, light red, biconvex and film-coated with a triangle pointing down above a “10” marked on one side and “Xa” on the other side | Round, red, biconvex, and film-coated with a triangle pointing down above a “15” marked on one side and “Xa” on the other side | Triangle-shaped, dark red, and film-coated with a triangle pointing down above a “20” marked on one side and “Xa” on the other side | |
| Imprint code / Engraving / Debossment | Debossed with a triangle pointing down above a “10” marked on one side and “Xa” on the other side | Debossed with a triangle pointing down above a “15” marked on one side and “Xa” on the other side | Debossed with a triangle pointing down above a “20” marked on one side and “Xa” on the other side | |
| Score | no score | no score | no score | |
| Color | Light red | Red | Dark red | |
| Shape | ROUND | ROUND | TRIANGLE | |
| Dimension | 6mm | 6mm | 7mm | |
| Mfg by |
Janssen Pharmaceuticals (US) Bayer Pharma (EU) |
|||
| Mfg for | Janssen Pharmaceuticals (US) | |||
| Marketed by | Janssen Pharmaceuticals (US), Bayer Pharma (EU) | |||
| Distributed by | - | |||
| Application No. | Prod No | Patent No | Patent Expiration | Drug Substance Claim | Drug Product Claim | Patent Use Code | Delist Requested | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N022406 | 1 | 7592339 | December 11, 2020 | - | - | U - 1302 | - | Download |
| N022406 | 1 | 7157456 | August 28, 2024 | Y | Y | U - 1301 | - | Download |
| N022406 | 1 | 7157456 | August 28, 2024 | Y | Y | U - 1301 | - | Download |
| N022406 | 1 | 7585860 | December 11, 2020 | Y | - | - | - | Download |
| N022406 | 1 | 9415053 | November 13, 2024 | - | DP | U-1167 U-1200 U-1301 U-1302 U-1303 | - | Download |
| N022406 | 1 | 9539218 | February 17, 2034 | - | - | U-1953 U-1954 U-1955 U-1956 U-1957 | - | Download |
| USP Apparatus | Speed (RPMs) | Medium | Volume (mL) | Recommended Sampling Times (minutes) | Date Updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II (Paddle) | 75 | Acetate Buffer pH 4.5, 0.2% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) | 900 | 10, 15, 20, 30 and 45 | January 15, 2015 (For Rivaroxaban tablet 10MG) |
| II (Paddle) | 75 | Acetate Buffer pH 4.5, 0.4% SDS | 900 | 10, 15, 20, 30 and 45 | January 15, 2015 (For Rivaroxaban tablet 15MG and 20MG) |
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| FDA label | Download |
| FDA chemistry review | Download |
| FDA Pharmacology Review(s) | Download |
| FDA Clinical Pharmacology Biopharmaceutics Review(s) | Download |
| FDA BE Recommendation | Download |
| European Public Assessment Report | Download |
| Territory | Brand name / Generic company name | Link |
|---|---|---|
| EU | XARELTO | Download |
| UK | XARELTO Tablet 15 and 20MG | Download |
| US | XARELTO | Download |
| Exclusivity Code: Exclusivity Expiration are I - 660: Nov 2, 2015; I - 661: Nov 2, 2015 and I - 662: Nov 2, 2015 |
| www.accessdata.fda.gov, www.drugbank.ca, www.ema.europa.eu, www.medicines.org.uk, dailymed.nlm.nih.gov |
