| Active Ingredient | RIBOCICLIB |
|---|
| Drug Name | FDA Application No. | Company | Dosage Form;Route | Strength | RLD Strength | Original Approval or Tentative Approval Date |
Exclusivity Expiration (NCE) |
Exclusivity Expiration (ODE) |
Chemical Type |
Review Classification |
Marketing Status |
TE Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KISQALI | NDA#209092 | NOVARTIS PHARMS CORP | TABLET;ORAL | 200MG | 200MG | March 13, 2017 | Mar 13, 2022 | - | 1 New molecular entity (NME) | PRIORITY | Prescription | TBD |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Structural Formula |
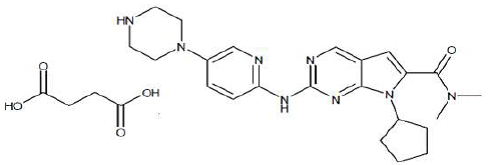 |
| Chemical Name | Butanedioic acid—7-cyclopentyl-N,N-dimethyl-2-{[5-(piperazin-1-yl) pyridin-2-yl]amino}-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide (1/1) |
| CAS No | 1211441-98-3 |
| Molecular Formula | C23H30N8O·C4H6O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 552.64 g/mol |
| Appearance | a light yellow to yellowish brown crystalline powder |
| Solubility | Soluble in acidic aqueous media, becoming less soluble as pH increases |
| Water Solubility | - |
| Polymorphism | Polymorphism has been observed for ribociclib succinate. Production of the correct polymorphic form is ensured by an XRPD method in the active substance specification. As described under the stability section, ribociclib succinate form A has been demonstrated to be stable and not to convert into other polymorphic forms under long term and accelerated stability studies when stored in the proposed packaging. |
| pKa (Strongest Acidic) | 11.59 (Predicted) |
| pKa (Strongest Basic) | 8.87 (Predicted) |
| Log P | 2.38 (Predicted) |
| Identification | IR, XRPD |
| Degradation | Stress tests were carried out in both solid and solution state. Samples were exposed to heat, heat and humidity, acid, base, humidity, and an oxidant. Impurities remained well within specification. No degradation was observed when solid ribociclib succinate was heated with oxygen |
| Hygroscopic | Slightly hygroscopic |
| Photostability study | Photostable |
| Melting Point | - |
| BCS Class | IV ( moderately permeable and low aqueous solubility) |
| Manufacture of API | - |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Indications and Usage | KISQALI® is indicated in combination with an aromatase inhibitor as initial endocrine-based therapy for the treatment of postmenopausal women with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer. |
| Dosage and Administration |
The recommended dose of KISQALI is 600 mg (three 200 mg film-coated tablets) taken orally, once daily for 21 consecutive days followed by 7 days off treatment resulting in a complete cycle of 28 days. KISQALI can be taken with or without food. Coadminister KISQALI with letrozole 2.5 mg taken once daily throughout the 28-day cycle. Refer to the full prescribing information of letrozole. For dosing and administration with other aromatase inhibitors refer to the applicable full prescribing information. Patients should take their dose of KISQALI and letrozole at approximately the same time each day, preferably in the morning. If the patient vomits after taking the dose, or misses a dose, no additional dose should be taken that day. The next prescribed dose should be taken at the usual time. KISQALI tablets should be swallowed whole (tablets should not be chewed, crushed or split prior to swallowing). No tablet should be ingested if it is broken, cracked, or otherwise not intact. Refer FDA Label for more information. |
| Mechanism of action |
KISQALI (ribociclib) is a kinase inhibitor. Ribociclib is an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4 and 6. These kinases are activated upon binding to Dcyclins and play a crucial role in signaling pathways which lead to cell cycle progression and cellular proliferation. The cyclin D-CDK4/6 complex regulates cell cycle progression through phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein (pRb). In vitro, ribociclib decreased pRb phosphorylation leading to arrest in the G1 phase of the cell cycle and reduced cell proliferation in breast cancer cell lines. In vivo, treatment with single agent ribociclib in a rat xenograft model with human tumor cells led to decreased tumor volumes, which correlated with inhibition of pRb phosphorylation. In studies using patient-derived estrogen receptor positive breast cancer xenograft models, combination of ribociclib and antiestrogen (e.g. letrozole) resulted in increased tumor growth inhibition compared to each drug alone. |
| Absorption |
Ribociclib exhibited over-proportional increases in exposure (peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) and area under the time concentration curve (AUC)) across the dose range of 50 mg to 1200 mg following both single dose and repeated doses. Following repeated 600 mg once daily administration, steady-state was generally achieved after 8 days and ribociclib accumulated with a geometric mean accumulation ratio of 2.51 (range: 0.972 to 6.40). The time to reach Cmax (Tmax) following ribociclib administration was between 1 and 4 hours. |
| Food Effect | Compared to the fasted state, oral administration of a single 600 mg dose of KISQALI film-coated tablet with a high-fat, high-calorie meal (approximately 800 to 1000 calories with ~50% calories from fat, ~35% calories from carbohydrates, and ~15% calories from protein) had no effect on the rate and extent of absorption of ribociclib (Cmax GMR: 1.00; 90% CI: 0.898, 1.11; AUCinf GMR: 1.06; 90% CI: 1.01, 1.12). |
| Distribution | Binding of ribociclib to human plasma proteins in vitro was approximately 70% and independent of concentration (10 to 10,000 ng/mL). Ribociclib was equally distributed between red blood cells and plasma with a mean in vivo blood-to plasma ratio of 1.04. The apparent volume of distribution at steady-state (Vss/F) was 1090 L based on population PK analysis. |
| Metabolism |
In vitro and in vivo studies indicated ribociclib undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism mainly via CYP3A4 in humans. Following oral administration of a single 600 mg dose of radio-labeled ribociclib to humans, the primary metabolic pathways for ribociclib involved oxidation (dealkylation, C and/or N-oxygenation, oxidation (-2H)) and combinations thereof. Phase II conjugates of ribociclib Phase I metabolites involved N-acetylation, sulfation, cysteine conjugation, glycosylation and glucuronidation. Ribociclib was the major circulating drug-derived entity in plasma (44%). The major circulating metabolites included metabolite M13 (CCI284, N-hydroxylation), M4 (LEQ803, N-demethylation), and M1 (secondary glucuronide), each representing an estimated 9%, 9%, and 8% of total radioactivity, and 22%, 20%, and 18% of ribociclib exposure. Clinical activity (pharmacological and safety) of ribociclib was due primarily to parent drug, with negligible contribution from circulating metabolites. Ribociclib was extensively metabolized with unchanged drug accounting for 17% and 12% in feces and urine, respectively. Metabolite LEQ803 was a significant metabolite in excreta and represented approximately 14% and 4% of the administered dose in feces and urine, respectively. Numerous other metabolites were detected in both feces and urine in minor amounts (≤ 3% of the administered dose). |
| Elimination |
The geometric mean plasma effective half-life (based on accumulation ratio) was 32.0 hours (63% CV) and the geometric mean apparent oral clearance (CL/F) was 25.5 L/hr (66% CV) at steady-state at 600 mg in patients with advanced cancer. The geometric mean apparent plasma terminal half-life (T1/2) of ribociclib ranged from 29.7 to 54.7 hours and geometric mean CL/F of ribociclib ranged from 39.9 to 77.5 L/hr at 600 mg across studies in healthy subjects. Ribociclib is eliminated mainly via feces, with a small contribution of the renal route. In 6 healthy male subjects, following a single oral dose of radio-labeled ribociclib, 92% of the total administered radioactive dose was recovered within 22 days; feces was the major route of excretion (69%), with 23% of the dose recovered in urine. |
| Peak plasma time (Tmax) | 1 and 4 hours |
| Half life | 32.0 hours |
| Bioavailability | - |
| Age, gender | Population PK analysis showed that there are no clinically relevant effects of age, body weight, gender, or race on the systemic exposure of ribociclib. |
| DMF | Status | Type | Submit Date | Holder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not Available | ||||
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Strength | 200 mg ribociclib (equivalent to 254.40 mg ribociclib succinate) |
| Excipients used | colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, hydroxypropylcellulose, magnesium stearate and microcrystalline cellulose |
| Composition of coating material | iron oxide black, iron oxide red, lecithin (soya) (0.344 mg), polyvinyl alcohol (partially hydrolysed), talc, titanium dioxide, and xanthan gum |
| Composition of caspule shell | - |
| Pharmaceutical Development | The active substance is a BCS class 4 molecule with moderate permeability. It is soluble in acidic media below pH 5.5 but solubility decreases at neutral and basic pH and stable in the solid form. A dry granulation process was developed in order to prevent changes in polymorphic form which could impact bioavailability. Suitable controls are in place to prevent detrimental solid form changes and ensure manufacturability. Excipients were chosen to enable manufacture of a robust film-coated tablet which performs adequately in vivo. Compatibility of the active substance with the chosen excipients was demonstrated through stability studies. |
| Manufacture of the product |
Blending of intra-granular components; roller compaction; milling and blending with extra-granular excipients; compression; film-coating |
| Tablet / Capsule Image | |
| Appearance | Film coated, light greyish violet, round, curved with beveled edges, debossed with “RIC” on one side and “NVR” on the other side. |
| Imprint code / Engraving / Debossment | Debossed with “RIC” on one side and “NVR” on the other side |
| Score | no score |
| Color | Light greyish violet |
| Shape | Round, curved with beveled edges |
| Dimension | 11 mm |
| Mfg by | Novartis Pharma GmbH (EU) |
| Mfg for | - |
| Marketed by | - |
| Distributed by | Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation |
| Application No. | Prod No | Patent No | Patent Expiration | Drug Substance Claim | Drug Product Claim | Patent Use Code | Delist Requested | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N209092 | 1 | 8324225 | June 17, 2028 | DS | DP | - | - | Download |
| N209092 | 1 | 8415355 | February 19, 2031 | DS | DP | - | - | Download |
| N209092 | 1 | 8685980 | May 25, 2030 | DS | DP | - | - | Download |
| N209092 | 1 | 8962630 | December 9, 2029 | - | - | U-1981 | - | Download |
| N209092 | 1 | 9193732 | November 9, 2031 | DS | DP | - | - | Download |
| N209092 | 1 | 9416136 | August 20, 2029 | - | - | U-1981 | - | Download |
| USP Apparatus | Speed (RPMs) | Medium | Volume (mL) | Recommended Sampling Times (minutes) | Date Updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II (Paddle) | 50 | 0.01N HCl (Degassed) | 900 | 10, 15, 20, 30, 45 and 60 | November 2, 2017 |
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| FDA label | Download |
| FDA chemistry review | Download |
| FDA Pharmacology Review(s) | |
| FDA Clinical Pharmacology Biopharmaceutics Review(s) | Download |
| FDA BE Recommendation | |
| European Public Assessment Report | Download |
| Territory | Brand name / Generic company name | Link |
|---|---|---|
| EU | KISQALI | Download |
| UK | KISQALI | Download |
| US | KISQALI | Download |
| Date of first authorisation/renewal of the authorisation in EU: 22 August 2017 |
| www.accessdata.fda.gov, www.drugbank.ca, www.ema.europa.eu, www.medicines.org.uk, dailymed.nlm.nih.gov |
