| Active Ingredient | IBRUTINIB |
|---|
| Drug Name | FDA Application No. | Company | Dosage Form;Route | Strength | RLD Strength | Original Approval or Tentative Approval Date |
Exclusivity Expiration (NCE) |
Exclusivity Expiration (ODE) |
Chemical Type |
Review Classification |
Marketing Status |
TE Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMBRUVICA | (NDA) 205552 | PHARMACYCLICS INC | CAPSULE;ORAL | 140MG, 70MG | 140MG | November 13, 2013 | November 13, 2018 | May 6, 2023 | 1 New molecular entity (NME) | P Priority review drug O Orphan drug | Prescription | None |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Structural Formula |
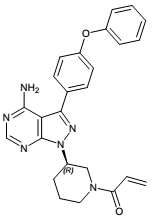 |
| Chemical Name | 1-[(3R)-3-[4-amino-3-(4-phenoxyphenyl)-1Hpyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-1-yl]-1-piperidinyl]-2-propen-1-one |
| CAS No | 936563-96-1 |
| Molecular Formula | C25H24N6O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 440.5 |
| Appearance | white to off-white solid |
| Solubility | It is practically insoluble in aqueous solutions of pH 4.5-8 and slightly soluble in HCl at pH 1.2. Ibrutinib is practically insoluble in non-polar solvents such as hexane and heptanes, sparingly soluble in ethyl acetate, ethanol and acetonitrile, soluble in acetone and methanol and freely soluble in N,N-dimethylformamide, tetrahydrofuran and dichloromethane. |
| Water Solubility | - |
| Polymorphism | Polymorphism was observed, three polymorphic forms of ibrutinib were identified and one of them which is the most thermodynamically stable is consistently formed during the active substance manufacturing process and used in the manufacturing of the finished product. |
| pKa (Strongest Acidic) | 19.7 (Predicted) |
| pKa (Strongest Basic) | 6.58 (Predicted) |
| Log P | 2.76 (Predicted) |
| Identification | IR, HPLC |
| Degradation | The forced degradation studies revealed that ibrutinib is sensitive to acid, alkaline and oxidative stress conditions. The drug substance was stable with respect to heat and light. Also, it has been shown that no change in polymorph of the drug substance occurs upon storage. |
| Hygroscopic | non-hygroscopic |
| Photostability study | Photo stable |
| Melting Point | - |
| BCS Class | II |
| Manufacture of API | Ibrutinib is manufactured in 6 main steps using commercially available well defined starting materials with acceptable specifications. |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Indications and Usage | IMBRUVICA is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult patients with: Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who have received at least one prior therapy Accelerated approval was granted for this indication based on overall response rate. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/Small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/Small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) with 17p deletion Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM) Marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) who require systemic therapy and have received at least one prior anti-CD20-based therapy Accelerated approval was granted for this indication based on overall response rate. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial. Chronic graft versus host disease (cGVHD) after failure of one or more lines of systemic therapy |
| Dosage and Administration |
MCL and MZL: 560 mg taken orally once daily CLL/SLL, WM, and cGVHD: 420 mg taken orally once daily Dose should be taken orally with a glass of water. Do not open, break, or chew the capsules. Do not cut, crush, or chew the tablets |
| Mechanism of action |
Ibrutinib is a small-molecule inhibitor of BTK. Ibrutinib forms a covalent bond with a cysteine residue in the BTK active site, leading to inhibition of BTK enzymatic activity. BTK is a signaling molecule of the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) and cytokine receptor pathways. BTK’s role in signaling through the B-cell surface receptors results in activation of pathways necessary for B-cell trafficking, chemotaxis, and adhesion. Nonclinical studies show that ibrutinib inhibits malignant B-cell proliferation and survival in vivo as well as cell migration and substrate adhesion in vitro. |
| Absorption |
Ibrutinib exposure increases with doses up to 840 mg (1.5 times the maximum approved recommended dosage) in patients with B-cell malignancies. The mean steady-state AUC (% coefficient of variation) observed in patients at 560 mg with MCL is 865 (69%) ngh/mL and with MZL is 978 (82%) ngh/mL, and in patients at 420 mg with CLL/SLL is 708 (71%) ngh/mL, with WM is 324 (48%) ngh/mL, and with cGVHD is 1159 (50%) ngh/mL.Steady-state concentrations of ibrutinib without CYP3A inhibitors were achieved with an accumulation ratio of 1 to 1.6 after 1 week of multiple daily doses of 420 mg or 560 mg. Absorption Absolute bioavailability of ibrutinib in fasted condition was 2.9% (90% CI: 2.1, 3.9) in healthy subjects. Ibrutinib is absorbed after oral administration with a median Tmax of 1 hour to 2 hour In vitro studies suggest that ibrutinib is not a substrate of p-glycoprotein (P-gp) or breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP). |
| Food Effect | The administration of IMBRUVICA with a high-fat and high-calorie meal (800 calories to 1,000 calories with approximately 50% of total caloric content of the meal from fat) increased ibrutinib Cmax by 2- to 4-fold and AUC by approximately 2-fold, compared with administration of ibrutinib after overnight fasting. |
| Distribution | Reversible binding of ibrutinib to human plasma protein in vitro was 97.3% with no concentration dependence in the range of 50 ng/mL to 1000 ng/mL. The volume of distribution (Vd) was 683 L, and the apparent volume of distribution at steady state (Vd,ss/F) was approximately 10,000 L. |
| Metabolism | Metabolism is the main route of elimination for ibrutinib. It is metabolized to several metabolites primarily by cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A and to a minor extent by CYP2D6. The active metabolite, PCI-45227, is a dihydrodiol metabolite with inhibitory activity towards BTK approximately 15 times lower than that of ibrutinib. The range of the mean metabolite to parent ratio for PCI-45227 at steady-state is 1 to 2.8. |
| Elimination |
Elimination Intravenous clearance was 62 L/h in fasted conditions and 76 L/h in fed conditions. In line with the high first-pass effect, the apparent oral clearance is 2000 L/h in fasted conditions and 1000 L/h in fed conditions. The half-life of ibrutinib is 4 hours to 6 hours. Excretion Ibrutinib, mainly in the form of metabolites, is eliminated primarily via feces. After a single oral administration of radiolabeled ibrutinib, 90% of radioactivity was excreted within 168 hours,with 80% excreted in the feces and less than 10% eliminated in urine. Unchanged ibrutinib accounted for 1% of the radiolabeled excreted dose in feces and none in urine, with the remainder of the excreted dose being metabolites. |
| Peak plasma time (Tmax) | 1 hour to 2 hours |
| Half life | 4 hours to 6 hours |
| Bioavailability | fasted condition was 2.9% |
| Age, gender | Age and sex have no clinically meaningful effect on ibrutinib pharmacokinetics. |
| DMF | Status | Type | Submit Date | Holder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30557 | A | II | May 31, 2016 | MSN LABORATORIES PRIVATE LTD (Amorphous) |
| 30746 | A | II | August 16, 2016 | PERRIGO API LTD |
| 30759 | A | II | July 31, 2016 | MSN LABORATORIES PRIVATE LTD (Form A) |
| 30925 | A | II | December 23, 2016 | SCINOPHARM TAIWAN LTD |
| 31199 | A | II | May 12, 2017 | FRESENIUS KABI ONCOLOGY LTD |
| 31547 | A | II | September 8, 2017 | SUN PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRIES LTD (Form S4) |
| 31631 | A | II | June 8, 2017 | TEVA PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRIES LTD |
| 31679 | A | II | May 5, 2017 | ESTEVE HUAYI PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD |
| 31689 | A | II | August 1, 2017 | HETERO LABS LTD (Form A) |
| 31728 | A | II | July 3, 2017 | CIPLA LTD |
| 31792 | A | II | June 23, 2017 | DR REDDYS LABORATORIES LTD |
| 31917 | A | II | July 20, 2017 | WISDOM PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD |
| 32122 | A | II | October 4, 2017 | SHILPA MEDICARE LTD |
| 32880 | A | II | July 2, 2018 | ALEMBIC PHARMACEUTICALS LTD IBRUTINIB |
| 32937 | A | II | August 17, 2018 | NATCO PHARMA LTD IBRUTINIB (IBN) |
| Parameters | Details | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | 70 MG | 140MG | |
| Excipients used | Croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium lauryl sulfate |
croscarmellose sodium (23MG), magnesium stearate (1.6MG), microcrystalline cellulose (151.4MG), sodium lauryl sulfate (14MG) | |
| Composition of coating material | - | ||
| Composition of caspule shell |
The capsule shell contains gelatin, titanium dioxide, yellow iron oxide and black ink. |
The capsule shell contains gelatin, titanium dioxide and black ink. | |
| Pharmaceutical Development |
A capsule formulation was selected as the oral solid dosage form due to ease of administration and high patient compliance. The limited solubility of ibrutinib in aqueous media has been one challenge in the efforts to obtain an orally bioavailable formulation and the formulation optimization approach has mainly focussed on enhancement of dissolution rate and solubility. The effect of different surfactants and micronization of the active substance on rate of absorption were evaluated in a pilot pharmaco-kinetic dog study comprising different formulations. Based on the results from this study the particle size of the active substance and the type and amount of surfactant to be used for further development were selected. The bioequivalence of the clinical formulation and the proposed commercial formulation is claimed based on an overall evaluation of the PK, efficacy/ safety, difference in formulations, dissolution profiles, all quality attributes and manufacturing process. A bioequivalence study was not performed. Results for Cmax and AUC obtained for the different formulations during individual clinical studies were evaluated, dissolution profiles compared and overall conclusion is presented claiming that the modification of formulations did not have an impact on the pharmacokinetics and efficacy data. |
||
| Manufacture of the product | The manufacturing process consists of six main steps including different blending steps, dry granulation, milling, encapsulation and packaging. In process controls are described and are considered adequate for this type of manufacturing process. | ||
| Tablet / Capsule Image |

|
||
| Appearance | Yellow opaque capsules, marked with “ibr 70 mg” in black ink | white opaque capsule is marked with “ibr 140 mg” in black ink | |
| Imprint code / Engraving / Debossment | marked with “ibr 70 mg” in black ink | marked with “ibr 140 mg” in black ink | |
| Score | no score | no score | |
| Color | Yellow opaque | WHITE | |
| Shape | CAPSULE | CAPSULE | |
| Dimension | 18 mm (Size 2) | 22mm (Size 0) | |
| Mfg by | - | Janssen Biotech, Inc. (EU) | |
| Mfg for | - | ||
| Marketed by | Pharmacyclics, Inc. (US), Janssen Biotech, Inc. (US, EU) | ||
| Distributed by | Pharmacyclics, Inc. (US) | ||
| Application No. | Prod No | Patent No | Patent Expiration | Drug Substance Claim | Drug Product Claim | Patent Use Code | Delist Requested | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N205552 | 1 | 7514444 | December 28, 2026 | Y | Y | - | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 8008309 | December 28, 2026 | Y | Y | - | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 8476284 | December 28, 2026 | - | - | U - 1456 | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 8476284 | December 28, 2026 | - | - | U - 1456 | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 8497277 | December 28, 2026 | - | - | U - 1650 | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 8497277 | December 28, 2026 | - | - | U - 1650 | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 8497277 | December 28, 2026 | - | - | U - 1650 | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 8697711 | December 28, 2026 | Y | Y | - | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 8703780 | December 28, 2026 | - | - | U - 1491 | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 8735403 | December 28, 2026 | Y | Y | - | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 8754090 | June 3, 2031 | - | - | U - 1456 | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 8754091 | December 28, 2026 | - | Y | - | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 8957079 | December 28, 2026 | Y | Y | - | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 8999999 | June 3, 2031 | - | - | U - 1684 | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 8999999 | June 3, 2031 | - | - | U - 1684 | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 9125889 | June 3, 2031 | - | - | U - 1745 | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 9181257 | December 28, 2026 | Y | Y | - | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 9296753 | October 30, 2033 | Y | Y | - | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 9540382 | August 18, 2033 | - | - | U-1456 U-1650 U-1684 U-1946 U-1947 | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 9713617 | June 3, 2033 | - | Y | - | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 9725455 | June 3, 2033 | Y | - | - | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 9795604 | October 24, 2034 | - | - | U-2150 | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 9801881 | June 3, 2031 | - | - | U-1491 | - | Download |
| N205552 | 1 | 9801883 | June 3, 2031 | - | - | U-2159 | - | Download |
| USP Apparatus | Speed (RPMs) | Medium | Volume (mL) | Recommended Sampling Times (minutes) | Date Updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II (Paddle) | 75 | 3.0% w/v Polysorbate 20 in 50 mM Phosphate Buffer, pH 6.8 | 900 | 5, 10, 20, 30 and 45 | June 25, 2015 |
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| FDA label | Download |
| FDA chemistry review | Download |
| FDA Pharmacology Review(s) | Download |
| FDA Clinical Pharmacology Biopharmaceutics Review(s) | Download |
| FDA BE Recommendation | Download |
| European Public Assessment Report | Download |
| Territory | Brand name / Generic company name | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Canada | IMBRUVICA | |
| EU | IMBRUVICA | Download |
| UK | IMBRUVICA | Download |
| US | IMBRUVICA | Download |
| Ibrutinib is marketed in to Canada, US and EU. 70 mg strength is available in US only. 70 mg approved on Dec 20, 2017 |
| www.accessdata.fda.gov, www.drugbank.ca, www.ema.europa.eu, www.medicines.org.uk, dailymed.nlm.nih.gov, www.drug.com |
