| Active Ingredient | FOSTAMATINIB DISODIUM |
|---|
| Drug Name | FDA Application No. | Company | Dosage Form;Route | Strength | RLD Strength | Original Approval or Tentative Approval Date |
Exclusivity Expiration (NCE) |
Exclusivity Expiration (ODE) |
Chemical Type |
Review Classification |
Marketing Status |
TE Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAVALISSE | 209299 | RIGEL PHARMS INC | TABLET;ORAL | EQ 100MG BASE, EQ 150MG BASE | EQ 150MG BASE | April 17, 2018 | April 17, 2023 | April 17, 2025 | Type 1 - New Molecular Entity | STANDARD; Orphan | Prescription | None |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Structural Formula |
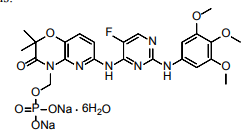 |
| Chemical Name | Disodium (6-[[5-fluoro-2-(3,4,5trimethoxyanilino) pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]-2,2-dimethyl-3-oxo-pyrido[3,2-b][1,4]oxazin-4-yl)methyl phosphate hexahydrate |
| CAS No | 901119-35-5 |
| Molecular Formula | C23H24FN6Na2O9P·6H2O |
| Molecular Weight | 732.52 |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder |
| Solubility | Practically insoluble in pH 1.2 aqueous buffer, slightly soluble in water, and soluble in methanol |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble in water |
| Polymorphism | - |
| pKa (Strongest Acidic) | 1.46 |
| pKa (Strongest Basic) | 2.71 |
| Log P | 1.46 |
| Identification | - |
| Degradation | - |
| Hygroscopic | - |
| Photostability study | - |
| Melting Point | - |
| BCS Class | - |
| Manufacture of API | - |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Indications and Usage | TAVALISSE is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in adult patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) who have had an insufficient response to a previous treatment. |
| Dosage and Administration |
Initiate TAVALISSE at 100 mg orally twice daily with or without food.After 4 weeks, increase to 150 mg twice daily, if needed, to achieve platelet count at least 50 x 109 /L as necessary to reduce the risk of bleeding. • Manage adverse reactions using dose reduction, interruption of treatment,or discontinuation. • Discontinue TAVALISSE after 12 weeks of treatment if the platelet count does not increase to a level sufficient to avoid clinically important bleeding |
| Mechanism of action | Fostamatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor with demonstrated activity against spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK). The major metabolite of fostamatinib, R406, inhibits signal transduction of Fc-activating receptors and B-cell receptor. The fostamatinib metabolite R406 reduces antibody-mediated destruction of platelets. |
| Absorption |
TAVALISSE is a prodrug that is converted in the gut to the major active metabolite, R406. Mean (±standard deviation [SD]) exposure estimates of R406 are 550 (± 270) ng/mL for Cmax and 7080 (± 2670)ng•h/mL for AUC. R406 exposure is approximately dose proportional up to 200 mg twice daily (1.3 timesthe 150 mg dosage). R406 accumulates approximately 2- to 3-fold upon twice daily dosing at 100–160mg (0.67 to 1.06 times the 150 mg dosage). After oral administration of TAVALISSE, the absolute bioavailability of R406 was 55%. The median tmax of R406 is approximately 1.5 hours (range: 1 to 4 hours). Negligible levels of fostamatinib were found in plasma. |
| Food Effect | Administration of TAVALISSE with a high-calorie, high-fat meal (deriving approximately 150, 250, and 500–600 calories from protein, carbohydrate, and fat, respectively) increased R406 AUC by 23% and Cmax by 15% |
| Distribution | In in vitro studies, the R406 is 98.3% protein bound in human plasma. The red blood cell to plasma concentration ratio is approximately 2.6. The mean (± SD) volume of distribution at steady-state of R406 is 256 (± 92) L. |
| Metabolism | TAVALISSE is metabolized in the gut by alkaline phosphatase to the major active metabolite, R406. R406 is extensively metabolized, primarily through pathways of CYP450-mediated oxidation (by CYP3A4) and glucuronidation (by UDP glucuronosyltransferase [UGT]1A9). R406 is the predominant moiety in the systemic circulation, and there was minimal exposure to any R406 metabolites. |
| Elimination |
The mean (± SD) terminal half-life of R406 is approximately 15 (± 4.3) hours. Excretion Following an oral dose of TAVALISSE, approximately 80% of the R406 metabolite is excreted in feces with approximately 20% excreted in the urine. The major component excreted in urine was R406 Nglucuronide. The major components excreted in feces were R406, O-desmethyl R406 and a metabolite produced by gut bacteria from the O-desmethyl metabolite of R406. |
| Peak plasma time (Tmax) | Median tmax of R406 is approximately 1.5 hours (range: 1 to 4 hours) |
| Half life | R406 is approximately 15 (± 4.3) hours |
| Bioavailability | Bioavailability of R406 was 55% |
| Age, gender | Population pharmacokinetics analyses indicate TAVALISSE is not altered based on age, sex, race/ethnicity. In addition, the pharmacokinetics of TAVALISSE is not altered in patients with renal impairment (creatinine clearance [CLcr] ≥ 30 to < 50 mL/min, estimated by Cockcroft Gault equation and end stage renal disease requiring dialysis), or hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A, B and C). |
| DMF | Status | Type | Submit Date | Holder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not Available | ||||
| Parameters | Details | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | EQ 100MG BASE | EQ 150MG BASE | |
| Excipients used | Mannitol, sodium bicarbonate, sodium starch glycolate,povidone, and magnesium stearate | ||
| Composition of coating material | Plyvinyl alcohol,titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol 3350, talc, iron oxide yellow, and iron oxide red | ||
| Composition of caspule shell | - | ||
| Pharmaceutical Development |
Each TAVALISSE oral tablet contains 100 mg or 150 mg fostamatinib, equivalent to 126.2 mg or 189.3 mg fostamatinib disodium hexahydrate, respectively. |
||
| Manufacture of the product | - | ||
| Tablet / Capsule Image | |||
| Appearance | Round, biconvex, orange, film-coated tablets debossed with “100” on one side and “R” on the reverse side | Oval, biconvex, orange, film-coated tablets debossed with “150” on one side and “R” on the reverse side | |
| Imprint code / Engraving / Debossment | Debossed with “100” on one side and “R” on the reverse side | Debossed with “150” on one side and “R” on the reverse side | |
| Score | No score | No score | |
| Color | Orange | Orange | |
| Shape | Round | Oval | |
| Dimension | 9 mm | 15 mm | |
| Mfg by | Patheon Whitby | ||
| Mfg for | Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | ||
| Marketed by | - | ||
| Distributed by | - | ||
| Application No. | Prod No | Patent No | Patent Expiration | Drug Substance Claim | Drug Product Claim | Patent Use Code | Delist Requested | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N209299 | 1 | 7449458 | September 4, 2026 | DS | - | - | - | Download |
| N209299 | 1 | 7538108 | March 28, 2026 | DS | - | U-2294 | - | Download |
| N209299 | 1 | 7989448 | June 12, 2026 | DS | - | U-2294 | - | Download |
| N209299 | 1 | 8163902 | June 17, 2026 | DS | - | U-2294 | - | Download |
| N209299 | 1 | 8211889 | January 19, 2026 | DS | - | - | - | Download |
| N209299 | 1 | 8263122 | November 24, 2030 | - | DP | - | - | Download |
| N209299 | 1 | 8445485 | June 17, 2026 | - | DP | - | - | Download |
| N209299 | 1 | 8652492 | November 6, 2028 | - | DP | - | - | Download |
| N209299 | 1 | 8771648 | July 27, 2032 | - | DP | - | - | Download |
| N209299 | 1 | 8912170 | June 17, 2026 | - | - | U-2294 | - | Download |
| N209299 | 1 | 8951504 | July 27, 2032 | - | - | U-2294 | - | Download |
| N209299 | 1 | 9266912 | January 19, 2026 | - | - | U-2294 | - | Download |
| N209299 | 1 | 9283238 | June 17, 2026 | - | - | U-2294 | - | Download |
| N209299 | 1 | 9737554 | January 19, 2026 | - | DP | - | - | Download |
| USP Apparatus | Speed (RPMs) | Medium | Volume (mL) | Recommended Sampling Times (minutes) | Date Updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not Available | |||||
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| FDA label | Download |
| FDA chemistry review | Download |
| FDA Pharmacology Review(s) | Download |
| FDA Clinical Pharmacology Biopharmaceutics Review(s) | Download |
| FDA BE Recommendation | |
| European Public Assessment Report |
| - |
| www.accessdata.fda.gov, www.drugbank.ca, www.ema.europa.eu, www.medicines.org.uk, dailymed.nlm.nih.gov |
