| Active Ingredient | FIDAXOMICIN |
|---|
| Drug Name | FDA Application No. | Company | Dosage Form;Route | Strength | RLD Strength | Original Approval or Tentative Approval Date |
Exclusivity Expiration (NCE) |
Exclusivity Expiration (ODE) |
Chemical Type |
Review Classification |
Marketing Status |
TE Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIFICID | (NDA) 201699 | CUBIST PHARMS LLC | TABLET;ORAL | 200MG | 200MG | May 27, 2011 | - | May 27, 2016 | 1 New molecular entity (NME) | P Priority review drug | Prescription | None |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Structural Formula |
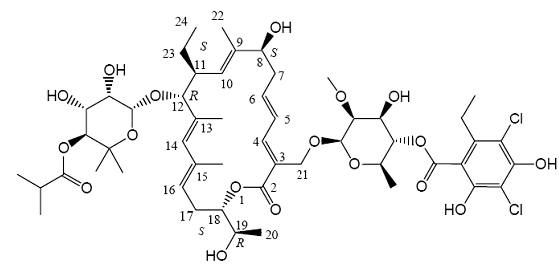 |
| Chemical Name | Oxacyclooctadeca-3,5,9,13,15-pentaen-2-one, 3-[[[6-deoxy-4-O-(3,5dichloro-2-ethyl-4,6-dihydroxybenzoyl)-2-O-methyl-β-D-mannopyranosyl]oxy]methyl] -12 [[6-deoxy-5-C-methyl-4-O-(2-methyl-1-oxopropyl)-β-D-lyxo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-11-ethyl8-hydroxy-18-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-9,13,15-trimethyl-, (3E,5E,8S,9E,11S,12R,13E,15E,18S) |
| CAS No | 873857-62-6 |
| Molecular Formula | C52H74Cl2O18 |
| Molecular Weight | 1058.04 |
| Appearance | a white to off-white powder |
| Solubility | It is practically insoluble in water. It is also freely soluble in tetrahydrofuran, dimethyl sulfoxide and methanol, soluble in acetone, sparingly soluble in ethanol, acetone, ethyl acetate, dichloromethane and acetonitrile, slightly soluble in isopropanol. |
| Water Solubility | 0.0125 mg/mL (Predicted) |
| Polymorphism | Only one polymorph form (polymorph form A) is routinely produced by the synthetic process described in the dossier and is used in the manufacture of the finished product. |
| pKa (Strongest Acidic) | 5.87 (Predicted) |
| pKa (Strongest Basic) | (Predicted) -1.4 |
| Log P | 5.59 (Predicted) |
| Identification | HPLC & TLC |
| Degradation | - |
| Hygroscopic | - |
| Photostability study | - |
| Melting Point | - |
| BCS Class | IV |
| Manufacture of API | Fidaxomicin drug substance is a purified fermentation product produced by the organism Dactylosporangium aurantiacum. The manufacturing process consists of inoculum expansion, production fermentation, isolation and purification. A full description of the manufacturing process was provided. Adequate controls of critical steps and intermediates are sufficient to ensure the quality of the active substance, and adequate specifications for starting materials, reagents, and solvents have been provided. The purified active substance is packed in low density polyethylene (LDPE) bags. Inner and outer LDPE bags with a silica gel sachet are placed inside a triple laminated aluminium bag which is placed inside of an HDPE container. |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Indications and Usage | To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of DIFICID and other antibacterialdrugs, DIFICID should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by Clostridium difficile. |
| Dosage and Administration | The recommended dose is one 200 mg DIFICID tablet orally twice daily for 10 days with or without food. |
| Mechanism of action | Fidaxomicin is an antibacterial drug. |
| Absorption |
The pharmacokinetic parameters of fidaxomicin and its main metabolite OP-1118 following a single dose of 200 mg in healthy adult males (N=14). Cmax of Fidaxomicin and OP-1118 are is 5.20 ± 2.81ng/mL and 12.0 ± 6.06ng/mL. Tmax of Fidaxomicin and OP-1118I are is 2.00 (1.00-5.00) hours and 1.02 (1.00-5.00) hours. Fidaxomicin has minimal systemic absorption following oral administration, with plasma concentrations of fidaxomicinand OP-1118 in the ng/mL range at the therapeutic dose. In fidaxomicin-treated patients from controlled trials, plasma concentrations of fidaxomicin and OP-1118 obtained within the Tmax window (1-5 hours) were approximately 2- to 6-fold higher than Cmax values in healthy adults. Following administration of DIFICID 200 mg twice daily for 10 days, OP-1118 plasma concentrations within the Tmax window were approximately 50%-80% higher than on Day 1, while concentrations of fidaxomicin were similar on Days 1 and 10. |
| Food Effect | In a food-effect study involving administrationof DIFICID to healthy adults (N=28) with a high-fat meal versus under fasting conditions, Cmax of fidaxomicin and OP-1118 decreased by 21.5% and 33.4%, respectively, while AUC0-t remained unchanged. This decrease in Cmax is not considered clinically significant, and thus, DIFICID may be administered with or without food. |
| Distribution | Fidaxomicin is mainly confined to the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration. In selected patients (N=8) treated with DIFICID 200 mg twice daily for 10 days from controlled trials, fecal concentrations of fidaxomicin and OP-1118 obtained within 24 hours of the last dose ranged from 639-2710 µg/g and 213-1210 µg/g, respectively. In contrast, plasma concentrations of fidaxomicin and OP-1118 within the Tmax window (1-5 hours) ranged 2-179 ng/mL and 10-829 ng/mL, respectively. |
| Metabolism | Fidaxomicin is primarily transformed by hydrolysis at the isobutyryl ester to form its main and microbiologically active metabolite, OP-1118. Metabolism of fidaxomicin and formation of OP-1118 are not dependent on cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes. At the therapeutic dose, OP-1118 was the predominant circulating compound in healthy adults, followed by fidaxomicin. |
| Elimination | Fidaxomicin is mainly excreted in feces. In one trial of healthy adults (N=11), more than 92% of the dose was recovered in the stool as fidaxomicin and OP-1118 following single doses of 200 mg and 300 mg. In another trial of healthy adults(N=6), 0.59% of the dose was recovered in urine as OP-1118 only following a single dose of 200 mg. |
| Peak plasma time (Tmax) | Tmax of Fidaxomicin and OP-1118I are is 2.00 (1.00-5.00) hours and 1.02 (1.00-5.00) hours. |
| Half life | T1/2 of Fidaxomicin and OP-1118I are is 11.7 ± 4.80 hours and 11.2 ± 3.01 hours. |
| Bioavailability | - |
| Age, gender |
Geriatric: In controlled trials of patients treated with DIFICID 200 mg twice daily for 10 days, mean and median values of fidaxomicin and OP-1118 plasma concentrations within the Tmax window (1-5 hours) were approximately 2- to4-fold higher in elderly patients (≥65 years of age) versus non-elderly patients (<65 years of age). Despite greater exposures in elderly patients, fidaxomicin and OP-1118 plasma concentrations remained in the ng/mL range. Gender :Plasma concentrations of fidaxomicin and OP-1118 within the Tmax window (1-5 hours) did not vary by gender in patients treated with DIFICID 200 mg twice daily for 10 days from controlled trials. No dose adjustment is recommended based on gender. |
| DMF | Status | Type | Submit Date | Holder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28803 | A | II | November 26, 2014 | BRIGHTGENE BIOMEDICAL TECHNOLOGY CO LTD |
| 29374 | A | II | September 29, 2015 | NORTH CHINA PHARMACEUTICAL HUASHENG CO LTD |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Strength | 200MG |
| Excipients used | microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, hydroxypropyl cellulose, butylated hydroxytoluene, sodium starch glycolate, magnesium stearate |
| Composition of coating material | polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide, talc, polyethylene glycol and lecithin (soy) |
| Composition of caspule shell | - |
| Pharmaceutical Development |
All information regarding the choice of the active substance and the excipients are sufficiently justified. The main aim of the pharmaceutical development was to formulate a conventional film-coated tablet, with a relatively rapid drug release containing 200 mg of fidaxomicin as active substance. An immediate release uncoated tablet containing 200 mg of fidaxomicin was developed for the first phase 3 clinical trial. During phase 3 the immediate release tablet was further optimized for longer shelf life. This optimized formulation was used in the second phase 3 clinical trial. |
| Manufacture of the product | The proposed commercial manufacturing process for the film-coated tablets involves standard technology and it is divided into the following steps: mixing, wet granulation, drying, milling, blending, compression, film coating, and packaging. The equipment used is commonly available in the pharmaceutical industry. The manufacturing process has been adequately described and granulation process has been identified as critical and optimised during the drug development. |
| Tablet / Capsule Image |

|
| Appearance | white to off-white film-coated, oblong tablets; each tablet is debossed with “FDX” on one side and “200” on the other side |
| Imprint code / Engraving / Debossment | debossed with “FDX” on one side and “200” on the other side |
| Score | no score |
| Color | white to off-white |
| Shape | OBLONG |
| Dimension | 14mm |
| Mfg by | Astellas Pharma (EU) |
| Mfg for | Optimer Pharmaceuticals (US) |
| Marketed by | Optimer Pharmaceuticals (US), Astellas Pharma (EU) |
| Distributed by | - |
| Application No. | Prod No | Patent No | Patent Expiration | Drug Substance Claim | Drug Product Claim | Patent Use Code | Delist Requested | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N201699 | 1 | 7906489 | March 4, 2027 | - | - | U - 319 | - | Download |
| N201699 | 1 | 8586551 | April 12, 2024 | Y | Y | - | - | Download |
| N201699 | 1 | 8859510 | July 31, 2027 | - | - | U - 319 | - | Download |
| USP Apparatus | Speed (RPMs) | Medium | Volume (mL) | Recommended Sampling Times (minutes) | Date Updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II (Paddle) | 75 | Water with 2% Tween 80 | 900 | 10, 15, 30, 45 and 60 | April 14, 2016 |
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| FDA label | Download |
| FDA chemistry review | Download |
| FDA Pharmacology Review(s) | Download |
| FDA Clinical Pharmacology Biopharmaceutics Review(s) | Download |
| FDA BE Recommendation | |
| European Public Assessment Report | Download |
| Territory | Brand name / Generic company name | Link |
|---|---|---|
| EU | DIFICID | Download |
| UK | DIFICID | Download |
| US | DIFICLIR | Download |
| - |
| www.accessdata.fda.gov, www.drugbank.ca, www.ema.europa.eu, www.medicines.org.uk, dailymed.nlm.nih.gov |
