| Active Ingredient | ELBASVIR; GRAZOPREVIR |
|---|
| Drug Name | FDA Application No. | Company | Dosage Form;Route | Strength | RLD Strength | Original Approval or Tentative Approval Date |
Exclusivity Expiration (NCE) |
Exclusivity Expiration (ODE) |
Chemical Type |
Review Classification |
Marketing Status |
TE Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZEPATIER | (NDA) 208261 | MERCK SHARP DOHME | TABLET;ORAL | 50MG; 100MG | 50MG; 100MG | January 28, 2016 | January 28, 2021 | _ | 1 New molecular entity (NME) | P Priority review drug | Prescription | None |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Structural Formula |
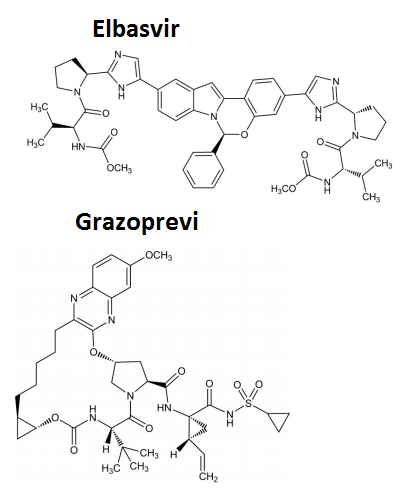 |
| Chemical Name | Elbasvir:Dimethyl N,N′-([(6S)-6-phenylindolo[1,2-c][1,3]benzoxazine-3,10-diyl]bis{1H-imidazole-5,2-diyl-(2S)-pyrrolidine-2,1-diyl[(2S)-3-methyl-1-oxobutane-1,2-diyl]})dicarbamate./ Grazoprevir:(1aR,5S,8S,10R,22aR)-N-[(1R,2S)-1-[(Cyclopropylsulfonamido)carbonyl]-2-ethenylcyclopropyl]-14-methoxy-5-(2-methylpropan-2-yl)-3,6-dioxo-1,1a,3,4,5,6,9,10,18,19,20,21,22,22a-tetradecahydro-8H-7,10-methanocyclopropa[18,19][1,10,3,6]dioxadiazacyclononadecino[11,12-b]quinoxaline-8-carboxamide |
| CAS No | Elbasvir: 1370468-36-2 / Grazoprevir: 1350514-68-9 |
| Molecular Formula | Elbasvir: C49H55N9O7 / Grazoprevir:C38H50N6O9S |
| Molecular Weight | Elbasvir: 882.02 / Grazoprevir: 766.90 |
| Appearance | Grazoprevir: white to off-white powder / Elbasvir: white to off-white powder |
| Solubility | Elbasvir: very slightly soluble in ethanol (0.2 mg per mL), but is very soluble in ethyl acetate and acetone / Grazoprevir: practically insoluble in water (less than 0.1 mg per mL) |
| Water Solubility | Elbasvir: practically insoluble in water (less than 0.1 mg per mL) / Grazoprevir:freely soluble in ethanol and some organic solvents (e.g., acetone, tetrahydrofuran and N,N-dimethylformamide) |
| Polymorphism | Grazoprevir: Polymorphism has been observed for the active substance. Experiments conducted confirmed that this free acid monohydrate (III) polymorphic form is the most stable form./ Elbasvir: exists as a weakly dibasic amorphous compound with no stable crystalline phase identified to date. remains amorphous after absorption and desorption of moisture. Extensive polymorph screening has not identified any non-solvated crystalline forms of elbasvi |
| pKa (Strongest Acidic) | Elbasvir: 12.42 / Grazoprevir:5.31 |
| pKa (Strongest Basic) | Elbasvir:5.39 / Grazoprevir:1.81 |
| Log P | Elbasvir: 6.17 / Grazoprevir:3.14 |
| Identification | Grazoprevir: IR, X-ray powder diffraction |
| Degradation | Grazoprevir: no trends or significant changes were observed under any of the conditions tested (150ºC, 0.1N HCl 40ºC, 0.1N NaOH 40ºC, 3% H2O2, and azobisisobutyronitrile at 5mM in methanol). / Elbasvir: Thermal/humidity and photolytic stress studies indicates that elbasvir requires storage at refrigerated conditions with desiccant and protected from light. |
| Hygroscopic | Grazoprevir: sensitive to moisture/ Elbasvir: hygroscopic |
| Photostability study | Grazoprevir: photosensitive in the solid state under ICH photostability stress conditions |
| Melting Point | - |
| BCS Class | - |
| Manufacture of API | Grazoprevir is synthesized in eight main steps using commercially available well defined starting materials with acceptable specifications. Grazoprevir is prepared by a convergent synthesis with eight total crystallizations/ Elbasvir is synthesized in six main steps using well defined starting materials with acceptable specifications. |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Indications and Usage | ZEPATIER is a fixed-dose combination product containing elbasvir, a hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5A inhibitor, and grazoprevir, an HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor, and is indicated with or without r bavirin for treatment of chronic HCV genotypes 1 or 4 infection in adults. |
| Dosage and Administration | Refer FDA label |
| Mechanism of action | ZEPATIER combines two direct-acting antiviral agents with distinct mechanisms of action and non-overlapping resistance profiles to target HCV at multiple steps in the viral lifecycle. Elbasvir is an inhibitor of HCV NS5A, which is essential for viral RNA replication and virion assembly. The mechanism of action of elbasvir has been characterized based on cell culture antiviral activity and drug resistance mapping studies. Grazoprevir is an inhibitor of the HCV NS3/4A protease which is necessary for the proteolytic cleavage of the HCV encoded polyprotein (into mature forms of the NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A, and NS5B proteins) and is essential for viral replication. In a biochemical assay, grazoprevir inhibited the proteolytic activity of the recombinant HCV genotype 1a, 1b, and 4a NS3/4A protease enzymes with IC50 values of 7 pM, 4 pM, and 62 pM, respectively. |
| Absorption |
Elbasvir AUC0-24 (ng•hr/mL): 1920 (1880, 1960) Cmax (ng/mL) :121 (118, 123) C24 (ng/mL):48.4 (47.3, 49.6) Grazoprevir AUC0-24 (ng•hr/mL): 1420 (1400, 1530) Cmax (ng/mL) : 165 (161, 176) C24 (ng/mL): 18.0 (17.8,19.9) Following administration of ZEPATIER to HCV-infected subjects, elbasvir peak concentrations occur at a median Tmax of 3 hours (range of 3 to 6 hours); grazoprevir peak concentrations occur at a median Tmax of 2 hours (range of 30 minutes to 3 hours). |
| Food Effect | Relative to fasting conditions, the administration of a single dose of ZEPATIER with a high-fat (900 kcal, 500 kcal from fat) meal to healthy subjects resulted in decreases in elbasvir AUC0-inf and Cmax of approximately 11% and 15%, respectively, and increases in grazoprevir AUC0-inf and Cmax of approximately 1.5-fold and 2.8-fold, respectively. These differences in elbasvir and grazoprevir exposure are not clinically relevant; therefore, ZEPATIER may be taken without regard to food |
| Distribution | Elbasvir and grazoprevir are extensively bound (greater than 99.9% and 98.8%, respectively) to human plasma proteins. Both elbasvir and grazoprevir bind to human serum albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein. Estimated apparent volume of distribution values of elbasvir and grazoprevir are approximately 680 L and 1250 L, respectively, based on population pharmacokinetic modeling. In preclinical distribution studies, elbasvir distributes into most tissues including the liver; whereas grazoprevir distributes predominantly to the liver likely facilitated by the active transport through the OATP1B1/3 liver uptake transporter. |
| Metabolism | Elbasvir and grazoprevir are partially eliminated by oxidative metabolism, primarily by CYP3A. No circulating metabolites of either elbasvir or grazoprevir were detected in human plasma. |
| Elimination | The geometric mean apparent terminal half-life for elbasvir (50 mg) and grazoprevir (100 mg) is approximately 24 and 31 hours, respectively, in HCV-infected subjects. The primary route of elimination of elbasvir and grazoprevir is through feces with almost all (greater than 90%) of radiolabeled dose recovered in feces compared to less than 1% in urine. |
| Peak plasma time (Tmax) | Elbasvir peak concentrations occur at a median Tmax of 3 hours (range of 3 to 6 hours); grazoprevir peak concentrations occur at a median Tmax of 2 hours (range of 30 minutes to 3 hours). |
| Half life | The geometric mean apparent terminal half-life for elbasvir (50 mg) and grazoprevir (100 mg) is approximately 24 and 31 hours, respectively, in HCV-infected subjects. |
| Bioavailability | - |
| Age, gender |
Pediatric Population The pharmacokinetics of ZEPATIER in pediatric patients less than 18 years of age have not been established. Geriatric Population In population pharmacokinetic analyses, elbasvir and grazoprevir AUCs are estimated to be 16% and 45% higher, respectively, in subjects at least 65 years of age compared to subjects less than 65 years of age. Gender In population pharmacokinetic analyses, elbasvir and grazoprevir AUCs are estimated to be 50% and 30% higher, respectively, in females compared to males. |
| DMF | Status | Type | Submit Date | Holder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | - | - |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Strength | 50MG; 100MG |
| Excipients used |
Colloidal silicon dioxide, copovidone, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium chloride, sodium lauryl sulfate, and vitamin E polyethylene glycol succinate |
| Composition of coating material | Carnauba wax, ferrosoferric oxide, hypromellose, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin |
| Composition of caspule shell | - |
| Pharmaceutical Development | Zepatier is supplied as a fixed-dose combination, film-coated tablet. Each tablet contains 50 mg of elbasvir and 100 mg of grazoprevir as active substances. Zepatier was designed as a robust, physically and chemically stable immediate-release solid dosage form using the considerations provided in the Target Product Profile. The pharmaceutical development of grazoprevir/elbasvir tablet was aimed at developing a solid oral dosage form that meets the quality requirements of the quality target product profile During development, appropriate QTPP categories were further translated into product CQAs The goal of the finished product development was to identify a formulation and manufacturing control strategy that robustly met these potential CQAs. The formulation strategy entailed the development of single entity formulations containing either grazoprevir or elbasvir active substances. The knowledge from the single entity development efforts was subsequently used for the development of the combination.Excipients were selected to provide a physically and chemically stable formulation with the intended biopharmaceutical properties. The active substances and the excipients were found to be compatible by evaluating the physical and chemical stability of the finished product. All excipients are compendial grade, with the exception of the film-coat (Opadry II); however, the components of the film-coating agent are compendial. All excipients are well known pharmaceutical ingredients and their quality is compliant with Ph. Eur standards. There are no novel excipients used in the finished product formulation. |
| Manufacture of the product | The manufacturing process consists of nine main steps: grazoprevir spray drying, grazoprevir blending and lubrication, grazoprevir roller compaction and milling, elbasvir spray drying, elbasvir blending and lubrication, elbasvir roller compaction and milling, final blending and lubrication of the grazoprevir and elbasvir granulations, tablet compression of grazoprevir/elbasvir granulations into monolithic fixed-dose combination (FDC) tablets, film coating, and packaging. The process is considered to be a standard manufacturing process. |
| Tablet / Capsule Image |
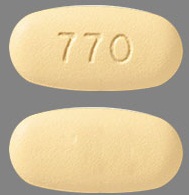
|
| Appearance | Beige, oval-shaped, film-coated, debossed with “770” on one side and plain on the other |
| Imprint code / Engraving / Debossment | Debossed with “770” on one side and plain on the other |
| Score | No score |
| Color | Beige |
| Shape | Oval-shaped |
| Dimension | 21 mm |
| Mfg by |
MSD International GmbH (US) Schering-Plough Labo N.V (EU) |
| Mfg for | Merck & Co |
| Marketed by | - |
| Distributed by | Merck Sharp & Dohme Ltd |
| Application No. | Prod No | Patent No | Patent Expiration | Drug Substance Claim | Drug Product Claim | Patent Use Code | Delist Requested | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (NDA) 208261 | 1 | 7973040 | July 24, 2029 | DS | DP | U-1813 | - | Download |
| (NDA) 208261 | 1 | 8871759 | May 4, 2031 | DS | DP | U-1813 | - | Download |
| USP Apparatus | Speed (RPMs) | Medium | Volume (mL) | Recommended Sampling Times (minutes) | Date Updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I (Basket) | 100 | Phosphate Buffer, pH 6.8 with 0.45% (w/v) Polysorbate 80 | 900 | 10, 15, 20, 30, 45 and 60 | 07/28/2016 |
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| FDA label | Download |
| FDA chemistry review | Download |
| FDA Pharmacology Review(s) | Download |
| FDA Clinical Pharmacology Biopharmaceutics Review(s) | Download |
| FDA BE Recommendation | Download |
| European Public Assessment Report | Download |
| Territory | Brand name / Generic company name | Link |
|---|---|---|
| EU | ZEPATIER | Download |
| UK | - | |
| US | ZEPATIER | Download |
| Grazoprevir: Particle size distribution and polymorphic form shall not affect the finished product performance Manufacture, characterisation and process controls. Approved in EU on 28/07/2016. |
| www.accessdata.fda.gov, www.drugbank.ca, www.ema.europa.eu, www.medicines.org.uk, dailymed.nlm.nih.gov |
