| Active Ingredient | DACOMITINIB |
|---|
| Drug Name | FDA Application No. | Company | Dosage Form;Route | Strength | RLD Strength | Original Approval or Tentative Approval Date |
Exclusivity Expiration (NCE) |
Exclusivity Expiration (ODE) |
Chemical Type |
Review Classification |
Marketing Status |
TE Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIZIMPRO | 211288 | PFIZER INC | TABLET;ORAL | 15 MG, 30 MG, 45 MG | 45 MG | September 27, 2018 | September 27, 2023 | September 27, 2025 | Type 1 - New Molecular Entity and Type 4 - New Combination | PRIORITY; Orphan | Prescription | None |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Structural Formula |
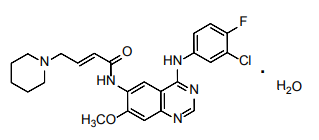 |
| Chemical Name | (2E)-N-{4-[(3-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl)amino]-7methoxyquinazolin-6-yl}-4-(piperidin-1-yl)but-2-enamide monohydrate |
| CAS No | 1110813-31-4 |
| Molecular Formula | C24H25ClFN5O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 487.95 Daltons |
| Appearance | White to pale yellow powder |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble in acetone and acetonitrile and sparingly soluble in acetic acid |
| Water Solubility | soluble in water at pH 1 at 25°C with solubility decreasingto less than 0.001 mg/mL at pH 8 |
| Polymorphism | The active substance shows polymorphism. Three relevant forms of dacomitinib have been identified:monohydrate Form A, monohydrate Form B and anhydrous Form C. Dacomitinib monohydrate Form A is the solid state form selected for development and commercialization. This is the thermodynamically favoured and predominant solid state form which was identified from extensive form screening experiments and crystallization studies across a diverse range of solvents and temperatures (4 to 75°C). |
| pKa (Strongest Acidic) | 12.5 |
| pKa (Strongest Basic) | 8.55 |
| Log P | 4.88 |
| Identification | IR |
| Degradation | Forced degradation studies were also conducted. Samples of dacomitinib active substance were exposed to acid, base, water, hydrogen peroxide, heat, humidity and simulated sunlight. The stress conditions studied were chosen to ensure that potential degradation pathways and major degradation products are elucidated and that the assay and purity methods are appropriately stability indicating. Most degradation was observed when dacomitinib active substance was stressed at high temperature. No degradation was observed under the neutral ,oxidative or basic conditions Minor degradation was observed for acidic and photostability .In the solid state, no degradation was observed at high temperature/high humidity No significant decrease in the assay value was observed when no degradation had occurred and acceptable mass balance was achieved for all conditions. The assay and purity method for dacomitinib active substance was shown to be specific, selective, and stability-indicating |
| Hygroscopic | non hygroscpic |
| Photostability study | Not light sensitive |
| Melting Point | 115.6 °C |
| BCS Class | II |
| Manufacture of API | The active substance is manufactured by a single manufacturer in a three-step convergent synthesis with one isolated intermediate. No alternative processes, reprocessing or recoveries have been proposed. Dacomitinib active substance is isolated as a monohydrate and is non-hygroscopic. The specified water content ensures the correct solid form is isolated. All dacomitinib active substance batches manufactured hroughout development were isolated as monohydrate Form A, with water contents within the proposed acceptance criterion. |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Indications and Usage | VIZIMPRO is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 19 deletion or exon 21 L858R substitution mutations as detected by an FDA-approved test. |
| Dosage and Administration | Recommended Dosage: 45 mg orally once daily with or without food |
| Mechanism of action | Dacomitinib is an irreversible inhibitor of the kinase activity of the human EGFR family (EGFR/HER1, HER2,and HER4) and certain EGFR activating mutations (exon 19 deletion or the exon 21 L858R substitution mutation). In vitro dacomitinib also inhibited the activity of DDR1, EPHA6, LCK, DDR2, and MNK1 at clinically relevant concentrations.Dacomitinib demonstrated dose-dependent inhibition of EGFR and HER2 autophosphorylation and tumor growth in mice bearing subcutaneously implanted human tumor xenografts driven by HER family targets including mutated EGFR. Dacomitinib also exhibited antitumor activity in orally-dosed mice bearing intracranial human tumor xenografts driven by EGFR amplifications. |
| Absorption |
The maximum dacomitinib plasma concentration (Cmax) and AUC at steady state increased proportionally over the dose range of VIZIMPRO 2 mg to 60 mg orally once daily (0.04 to 1.3 times the recommended dose) across dacomitinib studies in patients with cancer. At a dose of 45 mg orally once daily, the geometric mean [coefficient of variation (CV%)] Cmax was 108 ng/mL (35%) and the AUC0-24h was 2213 ng•h/mL (35%) at steady state in a dose-finding clinical study conducted in patients with solid tumors. Steady state was achieved within 14 days following repeated dosing and the estimated geometric mean (CV%) accumulation ratio was 5.7 (28%) based on AUC. Absorption The mean absolute bioavailability of dacomitinib is 80% after oral administration. The median dacomitinib time to reach maximum concentration (Tmax) occurred at approximately 6.0 hours (range 2.0 to 24 hours) after a single oral dose of VIZIMPRO 45 mg in patients with cancer |
| Food Effect | Administration of VIZIMPRO with a high-fat, high-calorie meal (approximately 800 to 1000 calories with 150, 250, and 500 to 600 calories from protein, carbohydrate and fat, respectively) had no clinically meaningful effect on dacomitinib pharmacokinetics. |
| Distribution | The geometric mean (CV%) volume of distribution of dacomitinib (Vss) was 1889 L (18%). In vitro binding of dacomitinib to human plasma proteins is approximately 98% and is independent of drug concentrations from 250 ng/mL to 1000 ng/mL. |
| Metabolism | Hepatic metabolism is the main route of clearance of dacomitinib, with oxidation and glutathione conjugation as the major pathways. Following oral administration of a single 45 mg dose of [14C] dacomitinib, the most abundant circulating metabolite was O-desmethyl dacomitinib, which had similar in vitro pharmacologic activity as dacomitinib. The steady-state plasma trough concentration of O-desmethyl dacomitinib ranges from 7.4% to 19% of the parent. In vitro studies indicated that cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2D6 was the major isozyme involved in the formation of O-desmethyl dacomitinib, while CYP3A4 contributed to the formation of other minor oxidative metabolites. |
| Elimination |
Following a single 45 mg oral dose of VIZIMPRO in patients with cancer, the mean (CV%) plasma half-life of dacomitinib was 70 hours (21%), and the geometric mean (CV%) apparent plasma clearance of dacomitinib was 24.9 L/h (36%). Excretion Following a single oral 45 mg dose of [14C] radiolabeled dacomitinib, 79% of the radioactivity was recovered in feces (20% as dacomitinib) and 3% in urine (<1% as dacomitinib). |
| Peak plasma time (Tmax) | Approximately 6.0 hours (range 2.0 to 24 hours) |
| Half life | 70 hours (21%) |
| Bioavailability | 80% |
| Age, gender | - |
| DMF | Status | Type | Submit Date | Holder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not Available | ||||
| Parameters | Details | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | 15 MG | 30 MG | 45 MG | |
| Excipients used | Lactose monohydrate (40 mg), microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate, and magnesium stearate | Lactose monohydrate (81 mg), microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate, and magnesium stearate | Lactose monohydrate (121 mg), microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate, and magnesium stearate | |
| Composition of coating material |
Opadry II® Blue 85F30716 containing: Polyvinyl alcohol – partially hydrolyzed, Talc, Titanium dioxide, Macrogol/PEG 3350, and FD&C Blue #2/Indigo Carmine Aluminum Lake |
|||
| Composition of caspule shell | NA | |||
| Pharmaceutical Development |
As indicated in the active substance section, dacomitinib Form A free-base monohydrate is the form that has been consistently isolated during the active substance manufacturing process and was selected for development and commercialization. Dacomitinib is a non-hygroscopic, white to pale yellow powder that is classified as BCS Class II (low solubility and high permeability) based on the Biopharmaceutical Classification System. Dacomitinib solubility is pH dependent, with solubility being highest under low pH gastric conditions in the fasted state. The impact of active substance particle size was an important consideration during finished product development, as dissolution of dacomitinib finished product may limit absorption. Therefore, particle size distribution was considered to be a CQA of the active substance.A range of active substance particle distributions were used to support clinical studies. Based on the results obtained in clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetic studies, dissolution testing, content uniformity and dissolution modelling, a particle size limit was included in the active substance specification. The proposed direct compression tablet formulation was based on a dry granulated formulation used for early clinical studies. The microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate, sodium starch glycolate and magnesium stearate used in the dry granulated formulation were maintained for the directly compressed tablet, and a non-functional aqueous film coat was applied |
|||
| Manufacture of the product | The manufacturing process consists of four main steps: blending, compression, film-coating and packaging.The manufacturing process is supported by a control strategy that assures each quality attribute is within the appropriate range required to deliver the desired efficacy, safety and quality of the finished product. | |||
| Tablet / Capsule Image |

|
|||
| Appearance | Blue film-coated, immediate release, round biconvex tablet, debossed with “Pfizer” on one side and “DCB15” on the other side. | Blue film-coated, immediate release, round biconvex tablet, debossed with “Pfizer” on one side and “DCB30” on the other side. | Blue film-coated, immediate release, round biconvex tablet, debossed with “Pfizer” on one side and “DCB45” on the other side. | |
| Imprint code / Engraving / Debossment | “Pfizer” on one side and “DCB15” on the other side. | “Pfizer” on one side and “DCB30” on the other side. | “Pfizer” on one side and “DCB45” on the other side. | |
| Score | No score | No score | No score | |
| Color | Blue | Blue | Blue | |
| Shape | Round biconvex tablet | Round biconvex tablet | Round biconvex tablet | |
| Dimension | 6.35 mm | 7.5 mm | 9.0 mm | |
| Mfg by | - | |||
| Mfg for | - | |||
| Marketed by | - | |||
| Distributed by | Pfizer Labs | |||
| Application No. | Prod No | Patent No | Patent Expiration | Drug Substance Claim | Drug Product Claim | Patent Use Code | Delist Requested | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N211288 | 1 | 7772243 | August 26, 2028 | DS | DP | - | - | Download |
| N211288 | 1 | 8623883 | May 5, 2025 | - | - | U-1403 | - | Download |
| USP Apparatus | Speed (RPMs) | Medium | Volume (mL) | Recommended Sampling Times (minutes) | Date Updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II (paddle) | 75 | Sodium acetate buffer pH 4.5 | 900 mL | Q point in 15 min | As per SBOA |
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| FDA label | Download |
| FDA chemistry review | Download |
| FDA Pharmacology Review(s) | Download |
| FDA Clinical Pharmacology Biopharmaceutics Review(s) | Download |
| FDA BE Recommendation | |
| European Public Assessment Report | Download |
| Territory | Brand name / Generic company name | Link |
|---|---|---|
| EU | VIZIMPRO | Download |
| UK | VIZIMPRO | Download |
| US | VIZIMPRO | Download |
| Shelf life: 5 years (EU) Date of first authorisation/renewal of the authorisation Date of first authorisation in EU: 02 April 2019 |
| www.accessdata.fda.gov, www.drugbank.ca, www.ema.europa.eu, www.medicines.org.uk, dailymed.nlm.nih.gov |
