| Active Ingredient | CINACALCET HYDROCHLORIDE |
|---|
| Drug Name | FDA Application No. | Company | Dosage Form;Route | Strength | RLD Strength | Original Approval or Tentative Approval Date |
Exclusivity Expiration (NCE) |
Exclusivity Expiration (ODE) |
Chemical Type |
Review Classification |
Marketing Status |
TE Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SENSIPAR | (NDA) 021688 | AMGEN | TABLET;ORAL | 30 MG, 60 MG, 90 MG | 90 MG | March 8, 2004 | _ | Nov 21, 2021 | 1 New molecular entity (NME) | P Priority review drug O Orphan drug | Prescription | None |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Structural Formula |
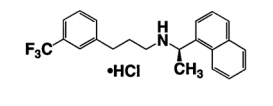 |
| Chemical Name | N-[1-(R)-(-)-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1-aminopropane hydrochloride |
| CAS No | 226256-56-0 |
| Molecular Formula | C22H22F3N⋅HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 393.9 g/mol (hydrochloride salt) and 357.4 g/mol (free base) |
| Appearance | White to off-white, crystalline solid |
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol or 95% ethanol |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble in water, very low aqueous solubility, especially at basic pH (<0.001 mg/ml) |
| Polymorphism | - |
| pKa (Strongest Acidic) | - |
| pKa (Strongest Basic) | 10.3 (Predicted) |
| Log P | 6.5 |
| Identification | IR, HPLC |
| Degradation | - |
| Hygroscopic | Non-hygroscopic |
| Photostability study | Not sensitive tolight |
| Melting Point | - |
| BCS Class | III |
| Manufacture of API | The manufacturing process has been adequately described, while the critical steps have been identified and are controlled by appropriate in process controls. The analytical methods used are sufficiently described and validated in accordance with the ICH guidelines.The impurities, including the S-enantiomer of cinacalcet, are well characterised and controlled. All specified impurities have been qualified in pre-clinical studies. The other impurities are controlled at the <0.1% level in the drug substance specification. The residual levels of solvents are adequatelycontrolled according to the ICH guidelines. |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Indications and Usage | Sensipar is a calcium-sensing receptor agonist indicated for: • Secondary Hyperparathyroidism (HPT) in adult patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) on dialysis. • Hypercalcemia in adult patients with Parathyroid Carcinoma (PC). • Hypercalcemia in adult patients with primary HPT for whom parathyroidectomy would be indicated on the basis of serum calcium levels, but who are unable to undergo parathyroidectomy. |
| Dosage and Administration |
For all indications, Sensipar should be taken with food or shortly after a meal and should always be taken whole and not divided. • Secondary HPT in patients with CKD on dialysis, o Starting dose is 30 mg once daily. o Titrate dose no more frequently than every 2 to 4 weeks through sequential doses of 30, 60, 90, 120, and 180 mg once daily as necessary to achieve targeted intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH) levels. o iPTH levels should be measured no earlier than 12 hours after most recent dose. • Hypercalcemia in patients with PC or hypercalcemia in patients with primary HPT. o Starting dose is 30 mg twice daily. o Titrate dose every 2 to 4 weeks through sequential doses of 30 mg twice daily, 60 mg twice daily, 90 mg twice daily, and 90 mg three or four times daily as necessary to normalize serum calcium levels. |
| Mechanism of action | The calcium-sensing receptor on the surface of the chief cell of the parathyroid gland is the principal regulator of PTH synthesis and secretion. Cinacalcet, the active ingredient in Sensipar, directly lowers PTH levels by increasing the sensitivity of the calcium-sensing receptor to extracellular calcium. The reduction in PTH is associated with a concomitant decrease in serum calcium levels |
| Absorption |
After oral administration of cinacalcet, Cmax is achieved in approximately 2 to 6 hours.The Cmax and AUC(0-infinite) of cinacalcet were increased by 65% and 50%, respectively, when cinacalcet was administered with a low-fat meal compared with fasting. After absorption, cinacalcet concentrations decline in a biphasic fashion with a terminal half-life of 30 to 40 hours. Steady-state drug levels are achieved within 7 days, and the mean accumulation ratio is approximately 2 with once daily oral administration. The median accumulation ratio is approximately 2 to 5 with twice daily oral administration. The AUC and Cmax of cinacalcet increase proportionally over the dose range of 30 to 180 mg once daily. The pharmacokinetic profile of cinacalcet does not change over time with once daily dosing of 30 to 180 mg. |
| Food Effect | Cinacalcet Cmax and AUC(0-infinite) were increased by 82% and 68%, respectively, following administration with a high-fat meal compared with fasting in healthy volunteers. |
| Distribution | The volume of distribution is approximately 1000 L, indicating extensive distribution. Cinacalcet is approximately 93% to 97% bound to plasma protein(s). The ratio of blood cinacalcet concentration to plasma cinacalcet concentration is 0.80 at a blood cinacalcet concentration of 10 ng/mL. |
| Metabolism | Cinacalcet is metabolized by multiple enzymes, primarily CYP3A4, CYP2D6, and CYP1A2. After administration of a 75 mg radiolabeled dose to healthy volunteers, cinacalcet was metabolized via: 1) oxidative N-dealkylation to hydrocinnamic acid and hydroxy-hydrocinnamic acid, which are further metabolized via β-oxidation and glycine conjugation; the oxidative N-dealkylation process also generates metabolites that contain the naphthalene ring; and 2) oxidation of the naphthalene ring on the parent drug forming dihydrodiols, which are further conjugated with glucuronic acid. The plasma concentrations of the major circulating metabolites, including the cinnamic acid derivatives and glucuronidated dihydrodiols, markedly exceed the parent drug concentrations. The hydrocinnamic acid metabolite and glucuronide conjugates have minimal or no calcimimetic activity. |
| Elimination | Renal excretion of metabolites was the primary route of elimination of radioactivity. Approximately 80% of the dose was recovered in the urine and 15% in the feces. |
| Peak plasma time (Tmax) | 2 to 6 hours |
| Half life | 30 to 40 hours |
| Bioavailability | - |
| Age, gender | The pharmacokinetic profile of cinacalcet in geriatric patients (age ≥ 65 years, n = 12) is similar to that for patients who are < 65 years of age (n = 268) |
| DMF | Status | Type | Submit Date | Holder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21264 | A | II | January 23, 2008 | TEVA PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRIES LTD |
| 21405 | A | II | March 6, 2008 | MEDICHEM MANUFACTURING MALTA LTD |
| 23910 | A | II | June 23, 2010 | ACTAVIS GROUP PTC EHF |
| 24297 | A | II | October 29, 2010 | IND SWIFT LABORATORIES LTD |
| 24881 | A | II | April 22, 2011 | MEGAFINE PHARMA P LTD |
| 25889 | A | II | March 29, 2012 | JUBILANT GENERICS LTD |
| 27211 | A | II | June 28, 2013 | DR REDDYS LABORATORIES LTD |
| 27364 | A | II | August 22, 2013 | AUROBINDO PHARMA LTD |
| 27592 | A | II | November 28, 2013 | SUN PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRIES LTD |
| 28051 | A | II | May 5, 2014 | CIPLA LTD |
| 28156 | A | II | March 27, 2014 | SHASUN PHARMACEUTICALS LTD |
| 28640 | A | II | September 15, 2014 | DISHMAN PHARMACEUTICALS AND CHEMICALS LTD |
| 28660 | A | II | July 11, 2015 | ENALTEC LABS PRIVATE LTD |
| 29147 | A | II | March 31, 2015 | LUPIN LTD |
| 29162 | A | II | March 25, 2015 | PIRAMAL ENTERPRISES LTD |
| 29399 | A | II | May 19, 2015 | HETERO DRUGS LTD |
| 29494 | A | II | June 24, 2015 | UQUIFA MEXICO SA DE CV |
| 29677 | A | II | September 7, 2015 | MACLEODS PHARMACEUTICALS LTD |
| 29737 | A | II | October 6, 2015 | CADILA HEALTHCARE LTD |
| 29866 | A | II | October 31, 2015 | MSN ORGANICS PRIVATE LTD |
| 30183 | A | II | December 30, 2015 | VIWIT PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD |
| 30385 | A | II | March 31, 2016 | UNICHEM LABORATORIES LTD |
| Parameters | Details | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | 60 MG | 90 MG | 30 MG | |
| Excipients used | pre-gelatinized starch, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, crospovidone, colloidal silicon dioxide and magnesium stearate | |||
| Composition of coating material | (Opadry® II green), clear film coat (Opadry® clear), and carnauba wax | |||
| Composition of caspule shell | - | |||
| Pharmaceutical Development |
30 mg, 60 mg, and 90 mg of cinacalcet as the free base equivalent (33 mg, 66 mg, and 99 mg as the hydrochloride salt, respectively). These properties underline the effect of the particle size and physical form on the dissolution and hence the bioavailability of the active substance and therefore need to be tightly controlled to ensure the clinical safety and efficacy of the medicinal product. The three strengths of the final commercial film-coated tablets have a proportionally identical composition. During the development of the commercial formulation, critical parameters for the in vivo perfo rmance of the dosage form have been identified. Different formulations have been used in the various clinical phases. These formulations have been well described and bridged to each other by bioequivalence studies. The in vivoresults have been used to dev elop a discriminating in vitro dissolution method. The excipients chosen are widely used in pharmaceutical preparations. Excipient compatibility studies were performed and demonstrated that there is no interaction with the active substance. |
|||
| Manufacture of the product | The manufacturing method used is a standard wet granulation process. Further manufacturing steps are wet milling, fluid bed drying and dry milling. After blending with extra-granular excipients and lubrication the granules are compressed. Coating with aqueous film coatings, waxing and tablet printing are the final operations. | |||
| Tablet / Capsule Image |
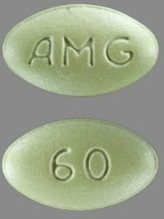
|
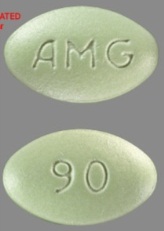
|

|
|
| Appearance | light-green, film-coated, oval-shaped tablets marked with “AMG” on one side and “60” on the opposite side | light-green, film-coated, oval-shaped tablets marked with “AMG” on one side and “90” on the opposite side | light-green, film-coated, oval-shaped tablets marked with “AMG” on one side and “30” on the opposite side | |
| Imprint code / Engraving / Debossment | Marked with “AMG” on one side and “60” on the opposite side | Marked with “AMG” on one side and “90” on the opposite side | Marked with “AMG” on one side and “30” on the opposite side | |
| Score | No score | No score | No score | |
| Color | Light-green | Light-green | Light-green | |
| Shape | Oval-shaped | Oval-shaped | Oval-shaped | |
| Dimension | 12 mm | - | 10 mm | |
| Mfg by | Amgen Inc (US/UK/EU) | |||
| Mfg for | - | |||
| Marketed by | Amgen Europe B.V (EU) | |||
| Distributed by | - | |||
| Application No. | Prod No | Patent No | Patent Expiration | Drug Substance Claim | Drug Product Claim | Patent Use Code | Delist Requested | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N021688 | 1 | 6011068 | March 8, 2018 | Y | Y | - | - | Download |
| N021688 | 1 | 6031003 | December 14, 2016 | - | - | U - 559 | - | Download |
| N021688 | 1 | 6211244 | October 23, 2015 | Y | Y | U - 560 | - | Download |
| N021688 | 1 | 6313146 | December 14, 2016 | Y | Y | - | - | Download |
| N021688 | 1 | 7829595 | September 22, 2026 | - | Y | U - 1098 | - | Download |
| USP Apparatus | Speed (RPMs) | Medium | Volume (mL) | Recommended Sampling Times (minutes) | Date Updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II (Paddle) | 75 | 0.05 N HCl | 900 | 10, 20, 30 and 45 | January 26, 2006 |
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| FDA label | Download |
| FDA chemistry review | Download |
| FDA Pharmacology Review(s) | Download |
| FDA Clinical Pharmacology Biopharmaceutics Review(s) | Download |
| FDA BE Recommendation | Download |
| European Public Assessment Report | Download |
| Territory | Brand name / Generic company name | Link |
|---|---|---|
| EU | Mimpara | Download |
| UK | Mimpara | Download |
| US | BARR (ANDA # 090476)* Tentative Approval | |
| US | MYLAN PHARMS INC (ANDA # 203422)* Tentative Approval | |
| US | SENSIPAR | Download |
| US | TEVA PHARMS (ANDA # 090539)* Tentative Approval |
| It has one chiral center having an R-absolute configuration. The R-enantiomer is the more potent enantiomer and has been shown to be responsible for pharmacodynamic activity. Date of first authorisation in EU/UK: 22 October 2004 |
| www.accessdata.fda.gov, www.drugbank.ca, www.ema.europa.eu, www.medicines.org.uk, dailymed.nlm.nih.gov |
