| Active Ingredient | BRIVARACETAM |
|---|
| Drug Name | FDA Application No. | Company | Dosage Form;Route | Strength | RLD Strength | Original Approval or Tentative Approval Date |
Exclusivity Expiration (NCE) |
Exclusivity Expiration (ODE) |
Chemical Type |
Review Classification |
Marketing Status |
TE Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRIVIACT | (NDA) 205836 | UCB INC | TABLET;ORAL | 10MG, 25MG, 50MG, 75MG, 100MG | 100MG | February 18, 2016 | February 18, 2021 | - | 1 New molecular entity (NME) | S Standard review drug | Prescription | None |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Structural Formula |
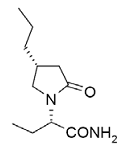 |
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-[(4R)-2-oxo-4-propyltetrahydro-1H-pyrrol-1-yl] butanamide |
| CAS No | 357336-20-0 |
| Molecular Formula | C11H20N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 212.29 |
| Appearance | a white to off-white crystalline powder |
| Solubility | It is very soluble in buffer (pH 1.2, 4.5, and 7.4), ethanol, methanol, and glacial acetic acid. It is freely soluble in acetonitrile and acetone and soluble in toluene. It is very slightly soluble in n-hexane. |
| Water Solubility | It is very soluble in water |
| Polymorphism | Two solid phases of brivaracetam are known. The manufacturing process generates only the desired solid phase 1. Solid phase 2 is an iso-solvate with non-polar organic molecules. Stability studies indicate that no solid phase interconversion occurs in the drug substance throughout the proposed re-test period. The second solid phase is, however, partially formed during tablet production but does not impact the performance of the finished product as dissolution is rapid and stability has been demonstrated. |
| pKa (Strongest Acidic) | - |
| pKa (Strongest Basic) | - |
| Log P | - |
| Identification | - |
| Degradation | Solid state stress testing was carried out at a range of temperatures and humidities. Brivaracetam is stable to heat exposure but degrades and picks up water when exposed to both high temperature and humidity. Brivaracetam degrades under strongly acidic and strongly basic conditions. It is considered stable under oxidative conditions. |
| Hygroscopic | non-hygroscopic |
| Photostability study | Photo stable |
| Melting Point | 72 to 77 °C (162 to 171 °F) |
| BCS Class | I |
| Manufacture of API | Brivaracetam is synthesized in two synthetic steps followed by resolution using well-defined starting materials with acceptable specifications. Different manufacturers are used for the individual steps. One chiral centre originates in a starting material whilst the other is generated during the synthetic process. The active substance is packaged in transparent LDPE bags |
| Parameters | Details |
|---|---|
| Indications and Usage | BRIVIACT is indicated as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial-onset seizures in patients 16 years of age and older with epilepsy. |
| Dosage and Administration |
When initiating treatment, gradual dose escalation is not required. The recommended starting dosage is 50 mg twice daily (100 mg per day). Based on individual patient tolerability and therapeutic response, the dosage may be adjusted down to 25 mg twice daily (50 mg per day) or up to 100 mg twice daily (200 mg per day). BRIVIACT injection may be used when oral administration is temporarily not feasible. BRIVIACT injection should be administered at the same dosage and same frequency as BRIVIACT tablets and oral solution. The clinical study experience with BRIVIACT injection is limited to 4 consecutive days of treatment. BRIVIACT tablets may be taken with or without food. BRIVIACT tablets should be swallowed whole with liquid. BRIVIACT tablets should not be chewed or crushed. |
| Mechanism of action | The precise mechanism by which BRIVIACT exerts its anticonvulsant activity is not known. Brivaracetam displays a high and selective affinity for synaptic vesicle protein 2A (SV2A) inthe brain, which may contribute to the anticonvulsant effect. |
| Absorption |
BRIVIACT tablets, oral solution, and injection can be used interchangeably. Brivaracetam exhibits linear and time-independent pharmacokinetics at the approved doses. Brivaracetam is highly permeable and is rapidly and almost completely absorbed after oral administration. Pharmacokinetics is dose-proportional from 10 to 600 mg (a range that extends beyond the minimum and maximum single-administration dose levels described in Dosage and Administration. The median Tmax for tablets taken without food is 1 hour (range 0.25 to 3 hours). |
| Food Effect | Co-administration with a high-fat meal slowed absorption, but the extent of absorption remained unchanged. Specifically, when a 50 mg tablet was administered with a high-fat meal, Cmax (maximum brivaracetam plasma concentration during a dose interval, an exposure metric) was decreased by 37% and Tmax was delayed by 3 hours, but AUC (area under the brivaracetam plasma concentration versus time curve, an exposure metric) was essentially unchanged (decreased by 5%). |
| Distribution | Brivaracetam is weakly bound to plasma proteins (≤20%). The volume of distribution is 0.5 L/kg, a value close to that of the total body water. Brivaracetam is rapidly and evenly distributed in most tissues. |
| Metabolism | Brivaracetam is primarily metabolized by hydrolysis of the amide moiety to form the corresponding carboxylic acid metabolite, and secondarily by hydroxylation on the propyl side chain to form the hydroxy metabolite. The hydrolysis reaction is mediated by hepatic and extra-hepatic amidase. The hydroxylation pathway is mediated primarily by CYP2C19. In human subjects possessing genetic variations in CYP2C19,production of the hydroxy metabolite is decreased 2-fold or 10-fold, while the blood level of brivaracetam itself is increased by 22% or 42%, respectively, in individuals with one or both mutated alleles. CYP2C19 poor metabolizers and patients using inhibitors of CYP2C19 may require dose reduction. An additional hydroxy acid metabolite is created by hydrolysis of the amide moiety on the hydroxy metabolite or hydroxylation of the propyl side chain on the carboxylic acid metabolite (mainly by CYP2C9).None of the 3 metabolites are pharmacologically active. |
| Elimination | Brivaracetam is eliminated primarily by metabolism and by excretion in the urine.More than 95% of the dose, including metabolites, is excreted in the urine within 72 hours after intake. Fecal excretion accounts for less than 1% of the dose. Less than 10% of the dose is excreted unchanged in the urine. Thirty-four percent of the dose is excreted as the carboxylic acid metabolite in urine. The terminal plasma half-life (t1/2) is approximately 9 hours. |
| Peak plasma time (Tmax) | 1 hour (range 0.25 to 3 hours) (Fast), Tmax was delayed by 3 hours with a high-fat meal. |
| Half life | 9 hours |
| Bioavailability | - |
| Age, gender |
In a study in elderly subjects (65 to 79 years old; creatinine clearance 53 to 98 mL/min/1.73 m²) receiving BRIVIACT 200 mg twice daily (2 times the highest recommended dosage), the plasma half-life of brivaracetam was 7.9 hours and 9.3 hours in the 65 to 75 and >75 years groups, respectively. The steady-state plasma clearance of brivaracetam was slightly lower (0.76 mL/min/kg) than in young healthy controls (0.83 mL/min/kg). There were no differences observed in the pharmacokinetics of brivaracetam between male and female subjects. A population pharmacokinetic analysis comparing Caucasian and non-Caucasian patients showed no significant pharmacokinetic difference. |
| DMF | Status | Type | Submit Date | Holder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not Available | ||||
| Parameters | Details | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | 25MG | 10MG | 50MG | 75MG | 100MG | |
| Excipients used |
croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, betadex (β-cyclodextrin), anhydrous lactose, magnesium stearate |
|||||
| Composition of coating material | polyvinyl alcohol, talc, polyethylene glycol 3350, titanium dioxide, yellow iron oxide, black iron oxide | polyvinyl alcohol, talc, polyethylene glycol 3350, titanium dioxide | polyvinyl alcohol, talc, polyethylene glycol 3350, titanium dioxide, yellow iron oxide, red iron oxide | polyvinyl alcohol, talc, polyethylene glycol 3350, titanium dioxide, yellow iron oxide, red iron oxide, black iron oxide | polyvinyl alcohol, talc, polyethylene glycol 3350, titanium dioxide, yellow iron oxide, black iron oxide | |
| Composition of caspule shell | - | |||||
| Pharmaceutical Development |
As such, film-coated tablets have been developed in five strengths: 10, 25, 50, 75 and 100 mg. The four highest strengths are made from a common blend and are thus quantitatively proportional, whilst the 10 mg tablet contains a lower proportion of active substance and different proportions of the same excipients. Tablets are debossed and distinguishable by size and colour. The active substance is highly soluble in physiologically relevant media and highly permeable and thus labelled as BCS I. There are no novel excipients used in an immediate release solid oral dosage form. It was found that partial conversion from polymorph I to polymorph II occurs on formulation. However, it was shown that this has no impact on the finished product dissolution characteristics and thus doesn’t affect bioavailability. The rapid dissolution of all formulations across the physiologically relevant pH range means that a disintegration test can be used instead of the standard dissolution test. Accordingly, no discriminatory dissolution method has been developed. Critical quality attributes of the finished product were identified as disintegration, assay, uniformity of dosage units and degradation products. |
|||||
| Manufacture of the product | The manufacturing process consists of five main steps: de-lumping and mixing of brivaracetam and intra-granular excipients; roller compaction; milling and blending with extra-granular excipients; compression to form tablet cores; film-coating. The process is considered to be a standard manufacturing process. | |||||
| Tablet / Capsule Image |
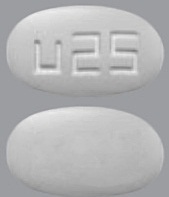
|

|
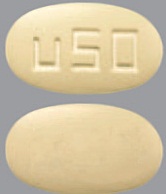
|

|
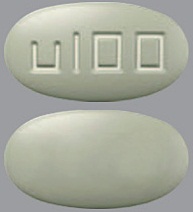
|
|
| Appearance | grey, oval, film-coated, and debossed with "u25" on one side | white to off white, round, film-coated, and debossed with "u10" on one side | yellow, oval, film-coated, and debossed with "u50" on one side | purple, oval, film-coated, and debossed with “u75” on one side | green-grey, oval, film-coated, and debossed with “u100” on one side | |
| Imprint code / Engraving / Debossment | debossed with "u25" on one side and plain on other side | debossed with "u10" on one side and plain on other side | debossed with "u50" on one side and plain on other side | debossed with "u75" on one side and plain on other side | debossed with "u100" on one side and plain on other side | |
| Score | no score | no score | no score | no score | no score | |
| Color | grey | white to off white | yellow | purple | green-grey | |
| Shape | OVAL | ROUND | OVAL | OVAL | OVAL | |
| Dimension | 8.9 mm x 5.0 mm | 6.5 mm | 11.7 mm x 6.6 mm | 13.0 mm x 7.3 mm | 14.5 mm x 8.1 mm | |
| Mfg by | UCB Pharma (EU) | |||||
| Mfg for | - | |||||
| Marketed by | UCB Pharma (US, EU) | |||||
| Distributed by | - | |||||
| Application No. | Prod No | Patent No | Patent Expiration | Drug Substance Claim | Drug Product Claim | Patent Use Code | Delist Requested | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N205836 | 1 | 6911461 | February 21, 2021 | Y | Y | U - 1815 | - | Download |
| N205836 | 1 | 6784197 | February 21, 2021 | DS | DP | U-1815 | - | Download |
| N205836 | 1 | 8492416 | February 21, 2021 | - | - | U-1815 | - | Download |
| USP Apparatus | Speed (RPMs) | Medium | Volume (mL) | Recommended Sampling Times (minutes) | Date Updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II (Paddle | 50 | Phosphate Buffer, pH 6.4 | 2.5 and 5 mg tablets: 500 mL; 10, 25, 50, 75 and 100 mg tablets: 900 mL | 5, 10, 15, 20 and 30 | July 28, 2016 |
| Label | Link |
|---|---|
| FDA label | Download |
| FDA chemistry review | Download |
| FDA Pharmacology Review(s) | Download |
| FDA Clinical Pharmacology Biopharmaceutics Review(s) | Download |
| FDA BE Recommendation | |
| European Public Assessment Report | Download |
| Territory | Brand name / Generic company name | Link |
|---|---|---|
| EU | BRIVIACT | Download |
| UK | BRIVIACT | Download |
| US | BRIVIACT | Download |
| - |
| www.accessdata.fda.gov, www.drugbank.ca, www.ema.europa.eu, www.medicines.org.uk, dailymed.nlm.nih.gov |
